Geographical data Overview
The Geographical data node includes the configuration elements necessary to configure the behavior of a geolocation client apps such as SnapVue.
It supports geolocation, micro-geolocation and tracking features of PcVue.
Geographical data includes:
- Zones - A zone usually represents a real world location such as a room in a building or the area where a specific piece of equipment is installed. Zones can be organized in a hierarchy with parent and child zones. For example Building1.Floor1.Room1.Chiller1. Zones can also be configured to represent the functional breakdown of a large piece of equipment.
- Geo-tags - A geo-tag is a beacon, the detection of which determines a corresponding geographical zone. The main property of a geo-tag is its unique ID. By associating a geo-tag with a zone, the PcVue server can determine the location of the connected user. The following geo-tag types are supported.
- NFC tags (Near Field Communication),
- QR codes,
- Bluetooth Low Energy beacons (BLE),
- Wi-Fi access points,
- GPS location. Not strictly speaking a geo-tag but may be used if geo-tags are found.
- Actions - An action, for example display a Mimic, that the user of a SnapVue client can execute. Actions are added to zones thereby determining what a user can visualize and execute when they have been determined to be in a particular zone. Actions can be cascaded from the parent zone by all child zones.
Using zones to represent the real world
A zone and the hierarchy of zones can be used in a variety of ways to support operational needs in different types of systems. The table below describes the 3 main drivers for designing the hierarchy of zones.
| Type of system | Operational need | What a zone represents |
| Infrastructure monitoring and other geographically distributed systems | Outdoor locations to identify remote sites. Lone workers tracking. Locate users while on site. |
The root part of the hierarchy includes zones corresponding to the different sites, with their GPS coordinates. Children zones matches a geographical and/or functional breakdown of sites, including associated geo-tags for the micro-geolocation of users by proximity to a given piece of equipment. |
| Building management systems | Indoor locations to identify areas on a site and within buildings. Locate users while on site or within buildings. |
Zones matches a physical and logical breakdown of buildings, including associated geo-tags for the micro-geolocation of users by proximity to a given piece of equipment or room (building, floors, zones or rooms). |
| Industrial equipment monitoring, manufacturing, factory automation | Indoor locations to identify areas on a site and within a factory. Locate users while on site or within the factory. |
Zones matches a physical and logical breakdown of the industrial site (factory), including associated geo-tags for the micro-geolocation of users by proximity to a given piece of manufacturing. The functional breakdown can go further with zones used to represent equipment pieces such as a control panel, an electrical panel, the front or rear part of a machine, a motor control panel... |
In a system comprising several geographically distributed sites, the root part of the hierarchy is usually a set of zones corresponding to the different sites, with their GPS coordinates.
How the SnapVue client and the geolocation server operate together
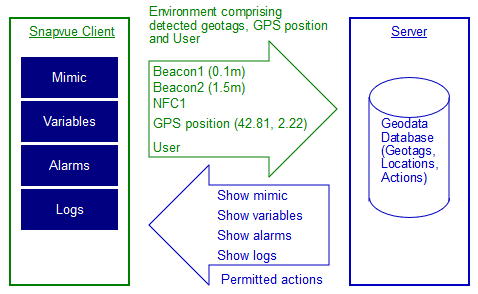
- The SnapVue client app runs on a mobile device such as an Android or iOS tablet or smart phone.
- The PcVue server software runs on a computer under Microsoft Windows.
- SnapVue and the server communicate using the IIS web server and deployed using the Web Deployment Console.
- SnapVue sends information to the server about the context of the connected user, detected geo-tags, and its GPS position (if available).
- The server determines the zone where the user is located using the geo-tags and sends the corresponding actions (for that zone and for any parent zone) to SnapVue.
- The SnapVue user is then able to visualize data and execute the actions appropriate to the zone context.
A zone's visibility to a user depends on the user's browsing rights as configured in the User Profile.