Web Based Architecture Examples
All in one
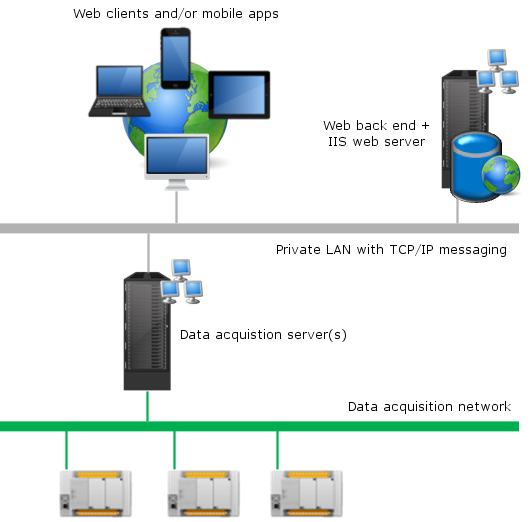
In this scenario the PcVue Web & Mobile back end station and the PcVue web server components are hosted and run on the same computer. ![]() Show picture
Show picture
Intended for simple deployment scenarios with the web and / or mobile client systems on the same network as the PcVue web back end station. Typically used when the network is private and fully isolated from outside access.
Should not be used when the network is open to incoming requests from outside networks or open for unprotected access from unknown devices. In particular, do not use this deployment strategy when access from web and mobile client on the Internet is required and there is no further means of network security (such as VPN-tunneling for instance) available.
Network isolation and DMZ
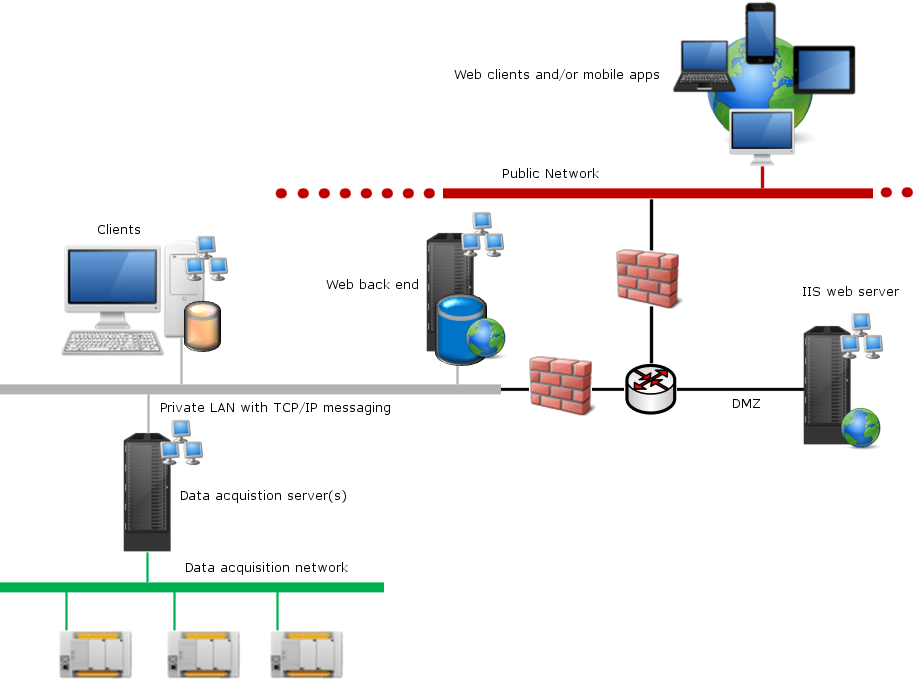
In this scenario, the PcVue Web & Mobile back end station and the web and / or mobile client are on different networks segregated by a DMZ. The inner network (LAN side of the DMZ) is seen as a private network. The outer network (WAN side of the DMZ) is a less trusted network and typically an office network or the internet. The PcVue web server components are hosted on a computer inside the DMZ and the Web back end station is on the private LAN. This architecture provides the best integration into IT infrastructures and allows for maximum compliance with IT policies and practices. ![]() Show picture
Show picture
This architecture is recommended whenever the web and/or mobile clients are outside of the industrial automation network. This architecture provides maximum deployment security, in line with IT network segregation practices, ensuring no un-controlled direct incoming connection from outside networks to the inner industrial automation network.
This architecture should be used whenever possible.
Simplified NAT
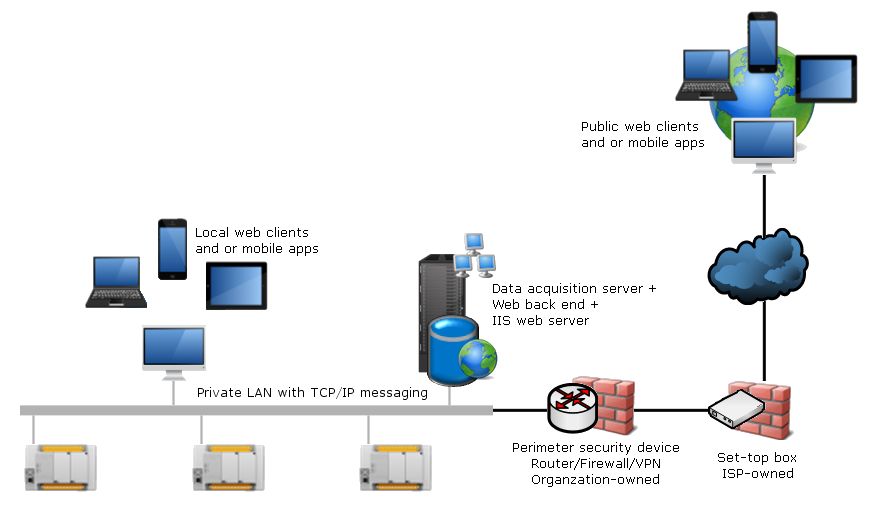
This scenario has a single private LAN where the Web server, Web & Mobile back end and, data acquisition server reside. Internet access is used to server a few remote web clients. The Web & Mobile clients are distributed across both sides of a NAT boundary provided by a set-top-box supplied and operated by the ISP.
This architecture is often the only option when a simple access from Internet is required with an ISP set-top box. Because you do not operate the ISP-owned device, you should have limited trust in it, and add your own network security appliance between the set-top-box and the web server. This appliance will act as a router/firewall and VPN server, and will the de-facto be the boundary of the network you control.
Although it is technically feasible to deploy this architecture as is, it is not recommended without further security measures.
- Use of a VPN and client address locking, in which case the architecture is logically equal to that described as All-In-One.
- Using the network perimeter’s dedicated DMZ port for establishing a dedicated network segment, in which case the architecture is a simplified version of Network Isolation and DMZ.
It is also recommended to separate the Web back end and the Web Server as described in Network Isolation and DMZ.