Management of variables.
WebVue support - Yes.
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Syntax |
| 1 | STATUS | 1 |
| 2 | MASK | 2 |
| 3 | UNMASK | 2 |
| 4 | ENABLE | 3 |
| 5 | DISABLE | 3 |
| 6 | LONGLABEL | 4 |
| 7 | ASSOCLABEL | 4 |
| 8 | SIMU | 5 |
| 9 | DOMAIN | 4 |
| 10 | NATURE | 4 |
| 11 | UNIT | 4 |
| 12 | NUMBER | 6 |
| 13 | THRESHOLD_GETTYPE | 3 |
| 14 | THRESHOLD_GETVALUE | 7 |
| 15 | THRESHOLD_SETVALUE | 8 |
| 22 | BATT | 9 |
| 23 | TATT | 10 |
| 24 | WRITE | 11 |
| 25 | LOCKTONODE | 12 |
| 26 | UNLOCKTONODE | 12 |
| 27 | FLOWPARAMTONODE | 13 |
| 28 | IMPORTBUFFER | 14 |
| 29 | IMPORTFILE | 15 |
| 30 | STARTWATCHLIST | 16 |
| 31 | STOPWATCHLIST | 17 |
| 32 | GET_LONG_IN_DB | 18 |
| 33 | GET_DOUBLE_IN_DB | 19 |
| 34 | GET_PHYSICAL_MIN | 19 |
| 35 | GET_PHYSICAL_MAX | 19 |
| 36 | GET_CONTROL_MIN | 19 |
| 37 | GET_CONTROL_MAX | 19 |
| 38 | SETBATT | 20 |
| 39 | SETTATT | 21 |
| 40 | SAVE | 22 |
| 41 | SETLONGLABEL | 25 |
| 42 | GET_ALARM_PRIORITY | 3 |
| 43 | GET_COMMAND_LEVEL | 3 |
| 44 | GET_CONTROL_LEVEL | 3 |
| 45 | GET_TEXT_LEVEL | 3 |
| 46 | GET_TYPE | 3 |
| 53 | GET_DEADBAND_TYPE | 3 |
| 54 | GET_DEADBAND_VALUE | 23 |
| 55 | SET_DEADBAND | 24 |
| 56 | TREND | 3 |
| 57 | GETSERVERSLIST | 4 |
| 60 | ADD_HMIBIT | 26 |
| 61 | ADD_HMIREG | 27 |
| 62 | ADD_HMITXT | 28 |
| 63 | REMOVE_HMIVAR | 29 |
| 64 | SETINVALID | 3 |
| 65 | TIMESTAMP | 30 |
| 66 | TRACE | 31 |
Arguments common to more than one mode
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
VarNname |
The name of a variable. Type STR. |
Syntax 1
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName, Property);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Property |
The property to be returned. Type INTEGER. 1 EXIST |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
1 |
STATUS |
Return the value corresponding to Property for the variable VarName: EXIST Return 1 if the variable exists,
else 0. 1 Masked by user
program 1 ENABLE Return 1 if the variable is inhibited,
else 0. 0 Valid timestamp set by PcVue. TEMPORARY_DB Return 1 if the variable is temporary, else 0. SIMU Return 1 if the variable is simulated, else 0. |
Syntax 2
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName, MaskLevel);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Action |
|
MaskLevel |
A 16-bit binary mask. 1 Masked by user
program 1 |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
2 |
MASK |
Set the mask of the variable using the given mask levels. |
|
3 |
UNMASK |
Clear the mask of the variable using the given mask levels. |
|
|
|
Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
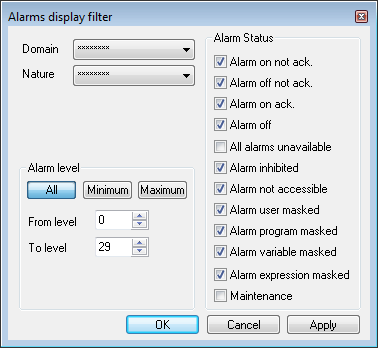
In the Alarm or Log Viewer, the behavior is as follows.
- To display an alarm masked using any combination of User program 1, User program 2, User program 3 and User program 4 the filter Alarm program masked must be ticked.
- To display an alarm masked using by operator the filter Alarm user masked must be ticked.
- To display an alarm masked using by dependency the filter Alarm variable masked must be ticked.
- To display an alarm masked using an expression the filter Alarm expression masked must be ticked.
 Show picture
Show picture
You can set or clear a combination of masks together by using the binary weight. For example, 9 would set the 1st and 4th mask bits.
Syntax 3
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName);
Return type: INTEGER.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
4 |
ENABLE |
Enable the variable VarName. |
|
5 |
DISABLE |
Disable the variable VarName. |
|
13 |
THRESHOLD_GETTYPE |
Return the threshold system of the variable VarName: 0 - No threshold. |
|
42 |
GET_ALARM_PRIORITY |
Return the alarm priority of the variable VarName. |
|
43 |
GET_COMMAND_LEVEL |
Return the command level of a bit variable VarName. |
|
44 |
GET_CONTROL_LEVEL |
Return the control level of a register variable VarName. |
|
45 |
GET_TEXT_LEVEL |
Return the control level of a text variable VarName. |
|
46 |
GET_TYPE |
Return the variable type of VarName: 1 Bit |
|
53 |
GET_DEADBAND_TYPE |
Return the deadband type of the variable VarName: -2 The variable does not exist or
is not a register. |
|
56 |
TREND |
Returns 1 if the variable VarName is trended, else 0. |
| 64 | SETINVALID |
Set the status of the variable VarName to NS. This mode can be used for any variable source. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
The modes ENABLE and DISABLE are the only way to change the inhibition status of an alarm. As for any other type of variable, such changes done by script will be logged if the alarm is archived and the log list is configured appropriately.
Syntax 4
StrVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName);
Return type: STR.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
6 |
LONGLABEL |
Return the long label (description) of the variable VarName. |
|
7 |
ASSOCLABEL |
Return the associated label of the variable VarName, corresponding to its current value. |
|
9 |
DOMAIN |
Return VarName's domain. |
|
10 |
NATURE |
Return VarName's nature. |
|
11 |
UNIT |
Return VarName's unit text (Register only). |
|
57 |
GETSERVERSLIST |
Returns the name of the list of producer stations of VarName. |
Syntax 5
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, Flag);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Flag |
A flag indicating the required operation. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
8 |
SIMU |
Enable and disable the simulation mode for the variable VarName: 0 for OFF When the simulation mode is ON the variable may be forced internally. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 6
LongVal = VARIABLE(Mode);
Return type: LONG.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
12 |
NUMBER |
Return the total number of variables configured in the project. |
Syntax 7
DblVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, Rank);
Return type: DOUBLE.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Rank |
A number between 0 and 3 specifying the rank of the threshold (1st, 2nd etc.). Type INTEGER. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
14 |
THRESHOLD_GETVALUE |
Return the value of the threshold specified by its rank. |
Syntax 8
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, Rank, Value[, Rank, Value] [, Rank, Value] [, Rank, Value][, SaveFlag]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Rank |
A number between 0 and 3 specifying the threshold (1st, 2ndetc.). Type INTEGER. Any thresholds that are omitted remain unchanged. |
|
Value |
A value for the threshold. |
|
SaveFlag |
When set to 1, indicates that the threshold change should be permanent and saved when the PcVue software is shut down. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
15 |
THRESHOLD_SETVALUE |
Assign a new value Value to the threshold specified by Rank for the variable VarName. The value given is checked: With the maximum and minimum value of the
variable. Return: 1 if successful, else 0 (out of range etc.). If successful, thresholds are recalculated, and threshold variables are updated accordingly. |
Syntax 9
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, BattNum);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
BattNum |
The rank of a binary attribute. Range 1 to 30. Type INTEGER. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
22 |
BATT |
Return the value of the binary attribute BattNum. |
Syntax 10
StrVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, TattNum);
Return type: STR.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
TattNum |
The number of a text attribute. Type INTEGER. Range 1 to 16. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
23 |
TATT |
Return the text attribute TattNum of the variable VarName. This instruction can be used to retrieve the Domain (TattNum = 1) and the Nature (TattNum = 2) of the variable. |
Syntax 11
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, SubMode);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
SubMode |
A code indicating the action to be taken. Type INTEGER. 0 Inhibit forcing of variables not produced by the local station. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
24 |
WRITE |
Handling of writing requests on the local station. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
There are always two default values, 1 and 2 for software versions before 10.0 and values 1 and 3 for version 10.0 onwards.
Sub-modes 0 and 1 allow inhibiting or authorizing command sending from passive, redundant stations or a client station.
Sub-modes 2 and 3 are applicable to all variables (Internal, Equipment, OPC, BACnet etc.).
Sub-mode type 3 optimizes writing requests.
Sub-mode type 3 does not apply to recipes.
Syntax 12
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, StationNb);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
StationNb |
A station number. Type INTEGER. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
25 |
LOCKTONODE |
Locks (disables) change of value messages to the specified station. This is used on multi-station architecture projects using dial-up networking. |
|
26 |
UNLOCKTONODE |
Unlocks (enables) change of value messages to the specified station. This is used on multi-station architecture projects using dial-up networking. |
|
|
|
Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 13
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, StationNb, StopLimit, StartLimit, Filter);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
StationNb |
A station number. Type INTEGER. |
|
StopLimit |
Threshold on the number of variables in the LAN manager mailbox for the station StationNb at which network flow control stops. Type INTEGER. |
|
StartLimit |
Threshold on the number of variables in the LAN manager mailbox for the station StationNb at which network flow control starts. Type INTEGER. |
|
Filter |
A number representing the variable types to be affected by the flow control. Each variable type is represented by a binary weight. Type INTEGER. 1 For the regulation of bit variables. For example, a value of 7 enables flow regulation for bit, alarm and register variables. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
27 |
FLOWPARAMTONODE |
Change the flow regulation parameters for the specified station. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
The default settings (before use of the VARIABLE instruction) are:
StopLimit 10
StartLimit 1000
Filter 15
Syntax 14
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, Handle [,Flag, ResultVar, FileReport]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Handle |
The location of the memory buffer as returned by ALLOC_BUFFER. Type LONG. |
| Flag |
A flag indicating how configuration modifications should be distributed. Type INTEGER
|
| ResultVar |
The name of a variable that returns the status of the import. Type STR.
|
| FileReport |
The name of the file containing a report of the import. Type STR. Variable Import Report Format |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
28 |
IMPORTBUFFER |
Import modifications to configuration items associated with variables, e.g. variables, expressions, trends and events. In general, items can be added, modified and deleted. The items to import are retrieved from the buffer Handle. For further information, see the topic File syntax for VARIABLE mode IMPORTFILE and IMPORTBUFFER. The import makes a permanent change, the changes are saved. Return: 1 if Handle exists, else 0. |
This method is no longer recommended for configuration import. Instead, it is preferable to use the Smart Generator and the Generic XML Import.
Syntax 15
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, FileName [,Flag, ResultVar, FileReport, FileError]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
FileName |
The name of a text file that describes the configuration items. Type STR. File path is relative to the folder TP of the project. |
| Flag |
A flag indicating how configuration modifications should be distributed. Type INTEGER
|
| ResultVar |
The name of a variable that returns the status of the import. Type STR.
|
| FileReport | The name of the file containing a report of the import.Variable Import Report Format Type STR. |
| FileError | The name of the file containing a report of any syntax errors for the import. Default FORM.ERR in the LOG FILES folder. Type STR. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
29 |
IMPORTFILE |
Import modifications to configuration items associated with variables, e.g. variables, expressions, trends and events. In general, items can be added, modified and deleted. The items to import are retrieved from the file FileName. For further information, see the topic File syntax for VARIABLE mode IMPORTFILE and IMPORTBUFFER. The import makes a permanent change, that is the changes are saved. Return: 1 if the file exists, else 0. |
This method is no longer recommended for configuration import. Instead, it is preferable to use the Smart Generator and the Generic XML Import.
Syntax 16
LongVal = VARIABLE(Mode, Branch, Handle, ResultVar, Flag);
Return type: LONG.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Branch |
An optional branch to be used in conjunction with the variable names provided by the buffer. Type STR. |
|
Handle |
The location of a memory buffer containing a list of variable names. The maximum size of the buffer is 128 KB. Type LONG. The format of the buffer is a list of the variable names. Those with a branch have a prefix of '@', for instance: @VARNAME1 VARNAME2 VARNAME3 |
|
ResultVar |
The name of a bit variable. Type STR. |
|
Flag |
Either 0 or 1. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
30 |
STARTWATCHLIST |
The variables, the names of which are contained in the buffer Handle, are put on scan. When all variables from the list are available the value specified in Flag is written to the ResultVar variable. The mode STARTWACHLIST is usually used in conjunction with mode STOPWATCHLIST. Return: The handle of a memory buffer. Once the variable ResultVar is set to Flag, this buffer containing as the list of the variables successfully put on scan. |
|
|
|
Syntax 17
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, Handle);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Handle |
The handle of a memory buffer returned from the execution of the mode STARTWATCHLIST. Type LONG. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
31 |
STOPWATCHLIST |
Put a list of variables off scan. See mode STARTWATCHLIST for more information. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 18
LongVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName);
Return type: LONG.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
32 |
GET_LONG_IN_DB |
The real time value of the variable VarName is returned as a LONG. |
Syntax 19
DblVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName,);
Return type: DOUBLE.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
33 |
GET_DOUBLE_IN_DB |
The real time value of the variable VarName is returned as a DOUBLE. |
|
34 |
GET_PHYSICAL_MIN |
The physical minimum for the variable VarName is returned. |
|
35 |
GET_PHYSICAL_MAX |
The physical maximum for the variable VarName is returned. |
|
36 |
GET_CONTROL_MIN |
The control minimum for the variable VarName is returned. |
|
37 |
GET_CONTROL_MAX |
The control maximum for the variable VarName is returned. |
Syntax 20
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, Value);
Return type: Integer.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Value |
The new value of the Boolean attributes of the variable. Type: INTEGER, LONG, SINGLE, DOUBLE or CONST. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
38 |
SETBATT |
Changes the value of the binary attributes of the variable VarName. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 21
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, TattNb, Text);
Return type: Integer.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
TattNb |
A text attribute number in the range 3 to 16. Any numeric type |
|
Text |
The new value for the specified text attribute. Type STR. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
39 |
SETTATT |
Set a new value for the text attribute TattNb of the variable VarName. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
You cannot use mode SETTATT to change Domain or Nature (attributes 1 and 2).
Syntax 22
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, 0, NoDisplayBarGraph);
Return type: Integer.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
0 |
Reserved, always equal to 0. |
|
NoDisplayBarGraph |
0 Show progress bar (default). 1 Do not show progress bar. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
40 |
SAVE |
Save the variable configuration. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 23
SVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName);
Return type: SINGLE.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
54 |
GET_DEADBAND_VALUE |
Returns the deadband value of the variable. |
Syntax 24
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName, DBvalue, DBtype);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
DBvalue |
A new deadband value. Type DOUBLE. |
|
DBtype |
A new deadband type. Type INTEGER |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
55 |
SET_DEADBAND |
Set a new deadband value and type for the variable VarName. Return: -5 The variable does not exist or is not
a register. |
Syntax 25
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName, Lang0[, Lang1]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
|
Lang0 |
String for language 0. Type STR. |
|
Lang1 |
String for language 1. Optional. Type STR |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
41 |
SETLONGLABEL |
Change the VarNamevariable's Description property. If the project is configured as bilingual you can change the string for both language 0 and language 1. The change is permanent. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
Syntax 26
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName[, Scope [,Description_1[, Description_2[, AssocLabel]]]]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
| Scope | The scope of the variable: 0 = Session Context (default). 1 = Client Context. 2 = Local Station. |
|
Description_1 |
The description of the variable for language 0. Default value = "". Type STR |
|
Description_2 |
The description of the variable for language 1. Default value = "". Type STR |
| AssocLabel | The name of the associated label of the variable. Default value = "". Type STR |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
60 |
ADD_HMIBIT |
An HMI bit variable named VarName is created using the supplied properties. Return: |
Syntax 27
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName[, Scope [,Description_1[, Desciption_2[, AssocLabel[, Min[, Max[, Format_1[, Format_2[, Unit_1[, Unit_2]]]]]]]]]]]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
| Scope | The scope of the variable: 0 = Session Context (default). 1 = Client Context. 2 = Local Station. |
|
Description_1 |
The description of the variable for language 0. Default value = "". Type STR. |
|
Description_2 |
The description of the variable for language 1. Default value = "". Type STR. |
| AssocLabel | The name of the associated label of the variable. Default value = "". Type STR. |
| Min | The minimum value. Default value = 0. Any numeric type. |
| Max | The maximum value. Default value = 65535. Any numeric type. |
| Format_1 | The display format for language 0, for example ###.##. Default value = “”. Type STR. |
| Format_2 | The display format for language 1, for example ###.##. Default value = “”. Type STR. |
| Unit_1 | The unit for language 0, for example "DegC". Default value = “”. Type STR. |
| Unit_2 | The unit for language 1, for example "DegC". Default value = “”. Type STR. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
61 |
ADD_HMIREG |
An HMI register variable named VarName is created using the supplied properties. Return: |
Syntax 28
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName[, Scope [, Description_1[, Description_2[, AssocLabel[, TextSize]]]]]);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
| Scope | The scope for the variable: 0 = Session Context (default). 1 = Client Context. 2 = Local Station. |
|
Description_1 |
The description of the variable for language 0. Default value = "". Type STR. String for language 0. Type STR. |
|
Description_2 |
The description of the variable for language 1. Default value = "". Type STR. |
| AssocLabel | The name of the associated label of the variable. Default value = "". Type STR. |
| TextSize | The maximum length. Default value 132. Any numeric type. |
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
62 |
ADD_HMITXT |
An HMI text variable named VarName is created using the supplied properties. Return: |
Syntax 29
IntVal = VARIABLE (Mode, VarName);
Return type: INTEGER.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
63 |
REMOVE_HMIVAR |
Remove the HMI variable VarName. Return: |
Syntax 30
DblVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName);
Return type: DOUBLE.
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
65 |
TIMESTAMP |
Return the timestamp of the variable VarName in number of milliseconds since 01/01/1970 at 00:00:00.000. |
Syntax 31
IntVal = VARIABLE(Mode, VarName, ON/OFF);
Return type: INTEGER.
|
Argument |
Meaning |
| ON/OFF |
Flag to enable or disable tracing. The possible values are:
|
Execution
|
Mode |
Mnemonic |
Action |
|
66 |
TRACE |
Sets tracing ON or OFF for the variable VarName. Return: 1 if successful, else 0. |
A note about variable validity
In addition to having a value and a timestamp, each variable has a validity status. A variable which is invalid is displayed in a special way by any animations using it; for example, a register display will be replaced by a "?". Several conditions may cause a variable to be invalid and these may be divided into 3 main classes:
|
Cause |
Meaning |
|
Masking |
See the topic Masking by Program. |
|
Inhibition |
When a variable is inhibited, its scanning is abandoned. A variable is normally inhibited when the hardware associated with it fails. |
|
Inaccessible |
Inaccessibility is a condition that is detected automatically as a result of the external source of a variable, field device or other station producing the variable, becoming unavailable (lost network connection...). |
Examples
For mode 15, THRESHOLD_SETVALUE:
To set the 1st threshold of variable var1 to 100 and the 3rd threshold to 500, permanently:
intval = VARIABLE("THRESHOLD_SETVALUE","var1",0,100,2,500,1);
For mode 38, SETBATT:
To force the Boolean attributes of the variable int.b1 from the register variable int.b1.batt.
SUB SetBAtt()
VARIABLE("SETBATT", "int.b1", int.b1.batt);
END SUB
To force the third Boolean attribute of the variable int.b1 to 1 and the other bits to 0:
SUB SetBAtt3()
VARIABLE("SETBATT", "int.b1", 4);
END SUB
For mode 56, TREND:
PRINT("x1 is a trend variable");
PRINT(VARIABLE(56, "x1"));
PRINT("x2 is not a trend variable");
PRINT(VARIABLE("TREND", "x2"));
Results:
x1 is a trend variable
1
x2 is not a trend variable
0
For longer examples, select the Example link above.