A truly smart building goes far beyond a single function. It must cover a wide range of domains, including HVAC and thermal comfort, lighting, security and access control, video surveillance, energy management, and the operation of technical equipment. To address all these features effectively, it is often necessary to select the best solutions and providers in each field.
However, this multi-vendor approach introduces a major challenge: communication between devices and software from different brands, each relying on different standard protocols (KNX, BACnet, Modbus, MQTT, LON, OPC UA etc.) or specific ones. Without a unifying integration layer, these systems risk working in silos, limiting overall efficiency and consistency.
This is why choosing an open and flexible SCADA platform is essential. A modern SCADA system must be able to interface with any protocol, ensuring seamless interoperability, future-proof installations, and the ability to add new equipment or functionalities over time—without ever being locked into a single standard.
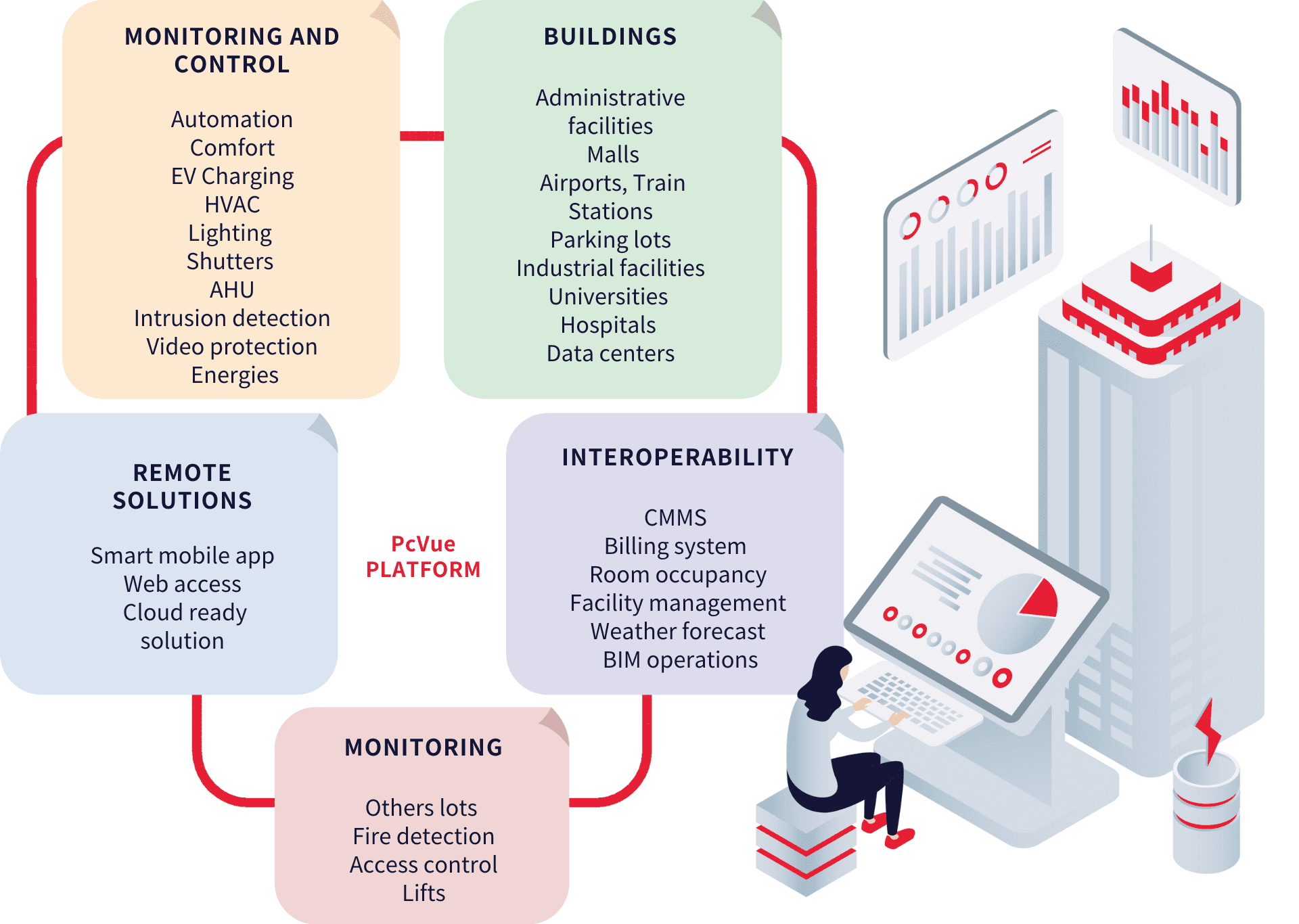
BACnet: Enabling Interoperability in Smart Buildings with SCADA
In the context of smart buildings, the integration of BACnet within a SCADA system plays a key role in ensuring smooth and standardized communication between heterogeneous subsystems such as HVAC, lighting, access control, and energy management. With its specific profiles, such as the BACnet Advanced Workstation (B-AWS) and the BACnet Operator Workstation (B-OWS), BACnet allows building managers to centralize supervision, simplify day-to-day operations, and optimize energy performance. By relying on this open protocol, SCADA systems provide interoperability across manufacturers, long-term system sustainability, and the flexibility needed to adapt to evolving requirements in increasingly connected environments.
ARC Informatique is an active member of BACnet association and has PcVue listed for tested B-AWS and B-OWS by the BTL (BACnet Testing Laboratories)

MQTT: Enabling Real-Time Data Communication in Smart Buildings

MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a lightweight protocol specifically designed for real-time data communication. It is ideal for IoT applications where bandwidth is limited, and latency must be minimized.
With PcVue’s support for MQTT, building managers can:
- – Monitor and control devices in real time, ensuring rapid response to changing conditions.
- – Improve operational efficiency by accessing up-to-date data from all connected systems.
- – Enable scalable IoT integration, allowing new sensors and devices to be added seamlessly.
By leveraging MQTT within a SCADA platform, smart buildings gain a responsive, efficient, and interconnected system, capable of handling dynamic environments while optimizing energy use and operational performance.
IoT: Connecting Devices for Hybrid Smart Building Solutions
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a central role in smart building applications, connecting various sensors and devices to collect and analyse data in real time.
In many cases, traditional wiring is impractical or too expensive. IoT devices using LPWAN (private or public networks) provide an ideal solution for numerous use cases:
- – Temperature or humidity sensors
- – Energy or water meters
- – Other environmental monitoring devices
The main challenge is the payload, meaning the data each IoT device produces, which is often non-standardized and difficult to integrate directly into SCADA systems.
With PcVue, this integration becomes straightforward: the platform can read, normalize, and process IoT data, combining it seamlessly with information from standard PLCs or field controllers. This enables a hybrid architecture that mixes IoT and traditional controllers, providing centralized and comprehensive supervision.
Benefits for smart buildings include:
- – Centralized data management from diverse sources
- – Unified monitoring and control within the SCADA system
- – Flexibility and scalability, allowing easy addition of new IoT sensors or PLCs
- – Energy and operational optimization through a holistic view of all systems
- – Reduce time and cost of implementation with no need of wires network
By leveraging IoT within a hybrid SCADA architecture, building managers can fully exploit wireless sensors while benefiting from standard controllers, resulting in a reliable, scalable, and intelligent smart building solution.
LON: A Robust Protocol for Building Automation
The LON (Local Operating Network) protocol is widely recognized as one of the historical standards in Building Management Systems (BMS) and industrial automation. Designed to enable decentralized and reliable communication between devices, LON is particularly well-suited for environments where robustness and long-term stability are critical, such as HVAC, lighting, and security systems.
With its distributed architecture, each LON node can make local decisions, ensuring resilience and service continuity even in the event of partial network failures. Its compatibility with a broad ecosystem of manufacturers has made LON a key protocol in existing buildings and critical infrastructures.
Integrating LON into a multi-protocol environment not only extends the value of existing installations but also enables seamless connectivity to modern systems through gateways and SDKs. This allows facility managers to maintain operational continuity while unlocking advanced strategies for energy optimization and centralized supervision.
KNX: Standardizing Building Automation within a SCADA
KNX is an international standardized protocol for building and home automation, ensuring compatibility and interoperability among devices from different manufacturers.
Within a SCADA system, integrating KNX allows building managers to:
- – Centralize control of automated systems such as lighting, HVAC, blinds, and more from a single interface.
- – Reduce complexity when managing devices from multiple brands and technologies.
- – Optimize monitoring and maintenance through a standardized platform that communicates seamlessly with all KNX devices.
- – Easily expand the system, adding new devices without disrupting existing operations.
By combining KNX with a SCADA platform like PcVue, building managers gain a streamlined, flexible, and scalable automation system, ensuring comfort, energy efficiency, and optimal control in smart buildings.
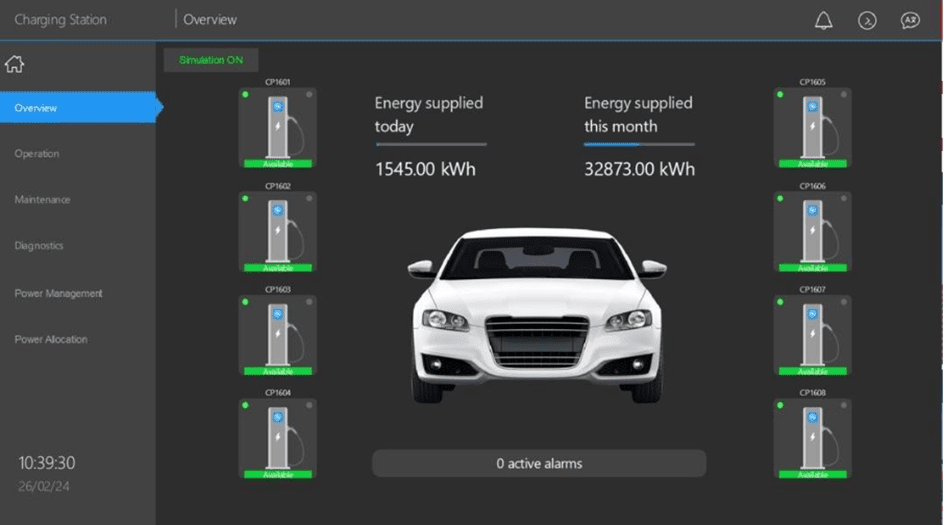
OCPP: A Key Standard for EV Charging Integration in Smart Buildings
In a smart building, energy management goes far beyond lighting, heating, or air conditioning—it now also includes electric vehicle charging. This is where the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) plays a crucial role, as it has become the leading communication standard between charging stations and supervisory systems. With OCPP, charging stations from different manufacturers can be integrated into a single SCADA or BMS platform, avoiding vendor lock-in. This interoperability ensures centralized and optimized management of charging infrastructures, fully aligned with other building systems such as energy management, consumption monitoring, and load shedding. By adopting OCPP, building operators gain not only maximum flexibility in equipment choices but also the ability to support the energy transition, seamlessly integrating e-mobility into their overall performance strategy.
TALQ: A Standard for Smart Outdoor and Indoor Lighting Management
The TALQ protocol was originally developed to standardize communication between Central Management Systems (CMS) and Outdoor Lighting Networks, enabling cities to implement smart street lighting solutions from multiple vendors without vendor lock-in. Over time, TALQ has evolved into a broader standard for smart city device management, covering not only lighting but also a wide range of urban services such as traffic monitoring, waste management, and environmental sensing.
In the context of smart buildings, TALQ offers a powerful reference for ensuring interoperability across diverse IoT and control systems, particularly where indoor and outdoor infrastructures converge. By providing a standardized framework for data exchange and device supervision, TALQ simplifies integration with SCADA and BMS platforms, enabling facility managers to centralize monitoring and optimize energy performance.
Adopting TALQ within a multi-protocol environment ensures that building operators and city managers alike can deploy scalable, future-proof solutions that remain open to innovation, vendor diversity, and evolving urban needs.
Simplified Multi-Protocol Implementation with PcVue
One of the key strengths of PcVue lies in its ability to natively support a multi-protocol implementation, covering all major standards highlighted in this article, such as BACnet, Modbus, OPC UA, and OCPP. With intuitive configuration wizards, deployment becomes straightforward: instead of complex development, a simple guided parameterization ensures seamless integration of building systems and devices. For more specific requirements, PcVue also enables the integration of additional protocols through dedicated SDKs and ADO.NET connectors, ensuring virtually unlimited interoperability. In addition, customers benefit from comprehensive support resources and continuous assistance from our sales, technical, and development teams, guaranteeing smooth implementation and reliable follow-up throughout the entire project.
Conclusion: Building the Foundation for True Smart Buildings
Interoperability is not just a technical requirement—it is the foundation of any truly smart building. By enabling different systems, devices, and protocols to work together seamlessly, building operators can unlock the full potential of modern technologies: optimized energy use, enhanced occupant comfort, stronger security, and reduced operational costs.
Choosing an open, protocol-agnostic SCADA platform ensures that buildings remain scalable, adaptable, and future-proof. As new technologies and standards emerge, an interoperable system guarantees the freedom to integrate the best solutions available—without being locked into one vendor or one technology.
Ultimately, interoperability transforms a building into a living, evolving ecosystem that can adapt to tomorrow’s challenges, creating long-term value for owners, operators, and occupants alike.
Further reading: