Do you work in the industrial or automation sector and often hear the term “SCADA” without fully understanding what it means? After reading this article, SCADA systems will no longer be a mystery! You’ll discover what a SCADA system is, how it works, what components it includes, and in which sectors it is used.
If you’re looking to better understand the role of SCADA in industry, you’re in the right place!
What is a SCADA?
The term SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition. Simply put, a SCADA system is a software platform that allows remote control of multiple sites—similar to home automation, but for industry. Imagine managing an amusement park: when it opens, you need to power on all the machines, make sure they’re functioning, and detect any issues. Doing this manually would be time-consuming. That’s where SCADA comes in. It centralizes all controls so everything can be managed from a single platform. In essence, SCADA enables you to:
- – Remotely monitor industrial installations;
- – Acquire and store real-time data;
- – Automatically or manually control equipment.
How does a SCADA System work?

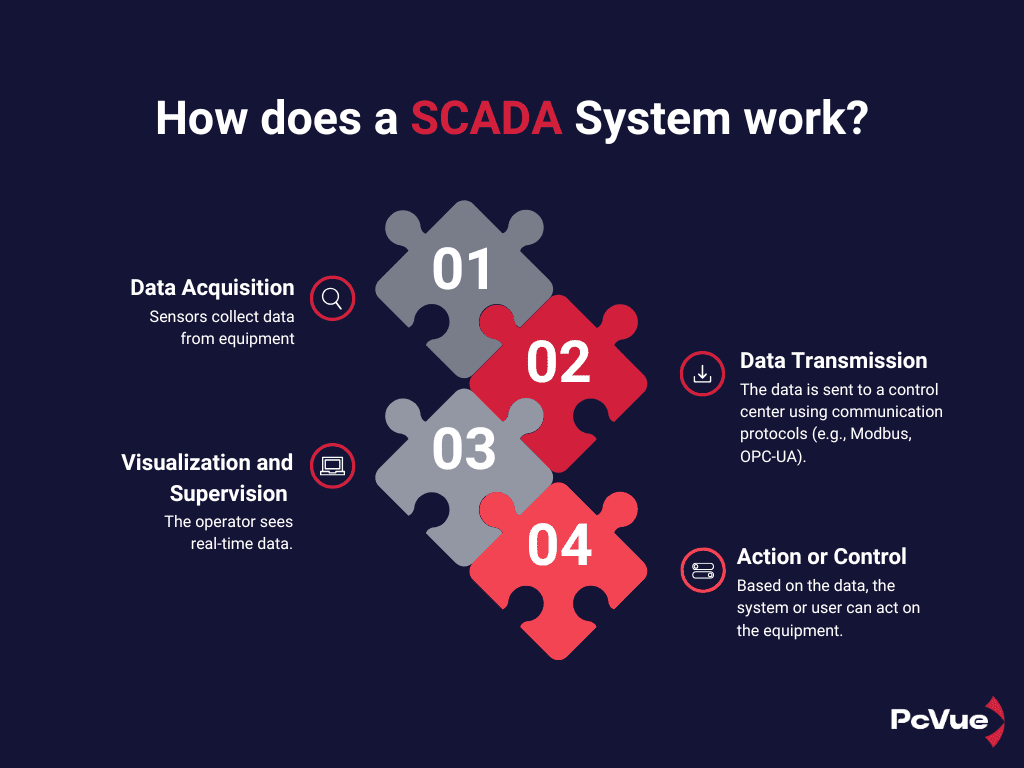
A SCADA system works in four main steps:
- 🧬 Data Acquisition via sensors, PLCs, or IoT: Sensors collect data from equipment.
Example : A sensor measures the water level in a tank and sends it to a PLC. - 🛣️ Data Transmission to a central server: The data is sent to a control center using communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, OPC-UA).
Example: The water level is sent every 5 seconds via Modbus TCP/IP.
- 🖼️ Visualization and Supervision via an HMI (Human-Machine Interface): The operator sees real-time data.
Example: The operator views the data as graphs, gauges, diagrams on the screen - 🕹️ Action or Control: Based on the data, the system or user can act on the equipment.
Example: The operator sees the tank is full and shuts off the pump.
This process gives a real-time overview of industrial site equipment.
👉 How Pcvue supervises water management at the Karian Dam in Indonesia
What is the purpose of using a SCADA System?
A SCADA system plays a central role by allowing remote control, monitoring, and optimization of installations. It serves primarily to:
- 🎠 Continuously monitor industrial processes
SCADA enables live visualization of the status of all connected equipment. Thanks to intuitive and interoperable graphical interfaces, operators can track processes in real-time, even on remote or hard-to-access sites.
- 🚨 React to alarms and/or anomalies
Equipment sends alerts when anomalies occur (e.g., high pressure, unusual temperature, low level). SCADA triggers visual and audible alarms, allowing quick operator response to avoid costly or dangerous incidents and reduce unplanned downtime.
- 💹 Optimize production performance
The data collected (consumption, efficiency, cycle time, etc.) helps identify weaknesses in the process. Adjustments can be made, energy losses reduced, and preventive maintenance scheduled. AI algorithms can also predict failures.
- 🪛 Reduce manual interventions
SCADA reduces the need for human presence in the field thanks to remote control and automation. This lowers operational costs and improves safety in hazardous environments (e.g., power plants, pumping stations).
- 📊 Generate reports and archives
SCADA continuously records data like measurements, alarms, commands, equipment status. These logs help with:
- – Performance reporting;
- – Incident tracing;
- – Compliance checks (audits, ISO, etc.).
A SCADA system is much more than just a dashboard: it’s a performance tool within the industry itself, enabling decisions to be made, reactions to be taken and processes to be improved, based on reliable, real-time data.
What are the Advantages of using a SCADA System?
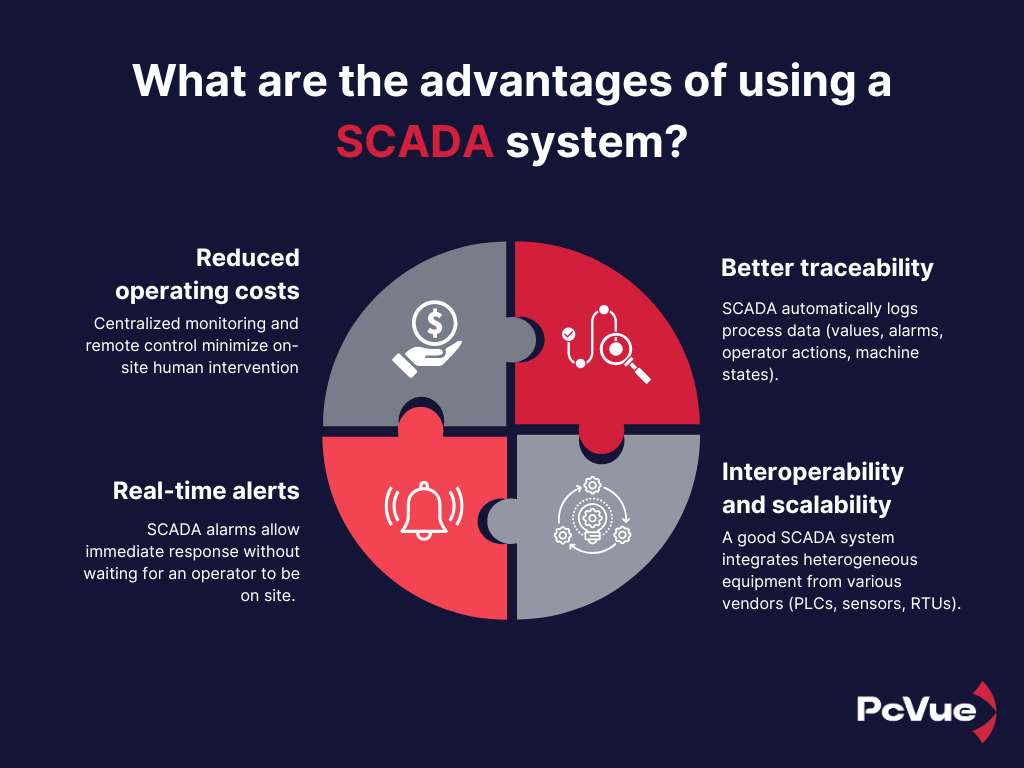
Adopting a SCADA system brings many technical, economic, and operational benefits for industrial sites, critical infrastructure, or distributed networks. Key advantages include:
- 💰 Reduced operating costs
Centralized monitoring and remote control minimize on-site human intervention. Continuous data collection supports preventive (vs corrective) maintenance, reducing unexpected breakdowns and extending equipment life.
Example : Early detection of a pump defect avoids costly production downtime.
- ⚡ Real-time alerts
SCADA alarms allow immediate response without waiting for an operator to be on site. The system instantly shows the source of the issue, speeding up diagnosis and decision-making.
Example : A pressure alert automatically stops a machine before any damage occurs.
- 🧾 Better traceability
SCADA automatically logs process data (values, alarms, operator actions, machine states). These records are essential for:
- Post-incident analysis ;
- Performance reports ;
- Audits or regulatory requirements;
Example : Logs explain why a pump started outside normal hours.
- 🔌 Interoperability and scalability
A good SCADA system integrates heterogeneous equipment from various vendors (PLCs, sensors, RTUs). It supports standard protocols (Modbus, OPC UA, DNP3, IEC 60870-5-104), making it easier to deploy and expand.
Example : A site can add new sensors or PLCs without reprogramming everything.
Examples of SCADA Applications
- Energy: Supervision of substations, solar parks, or wind farms.
👉 Discover a Success Story: Electrifying remote villages in Sarawak, Malaysia with PcVue SCADA - Water & Wastewater: Control of pumping stations, reservoirs, treatment plants.
👉 Discover a Success Story: How Pcvue platform supervises water management at the Karian Dam in Indonesia - Industry: Operation of automated production lines.
👉 Discover a Success Story: The case of USV Limited, a manufacturer of lifescience drugs - Transport: Management of tunnels, subways, traffic lights.
👉 Discover a Success Story about Toulouse tramway in France - Smart Buildings: Monitoring consumption, centralized technical management.
👉 Discover a Success Story: Large Hadron Collider at CERN - Data Center
👉 Discover a Success Story: PcVue in the new Data Center of TelecityGroup France - EV Charging
👉 Discover a Success Story: Monitoring the charging stations of the e-bus fleet of the city of Jena in Germany
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the difference between SCADA and DCS ?
Both systems supervise and control industrial installations, but:
– SCADA (Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition) is ideal for monitoring dispersed equipment (e.g., water/electricity networks, pipelines). It’s centralized and suitable for geographically large infrastructures.
– DCS (Distributed Control System) is used on a single site where ultra-fast and localized control is needed (e.g., refineries, chemical plants). It’s often distributed, with multiple controllers near machines.
- Can a SCADA be used on the web or mobile?
Yes. A SCADA can offer:
- A web interface accessible from a secure browser.
- A mobile app to view alarms, check data, or control equipment remotely.
This allows faster interventions without needing to be in the control room.
- Can SCADA run in the cloud?
Absolutely. SCADA solutions are moving toward cloud-based architectures, which offer:
- Secure access to data from anywhere;
- Better team collaboration;
- Lower infrastructure costs (fewer physical servers).
Enhanced cybersecurity is necessary, but this is becoming increasingly common.
- Are SCADA and AR/VR compatible?
Yes and it’s a promising emerging trend:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Technicians can see live data overlaid on equipment using tablets or smart glasses (e.g., temperature, state, alarms).
- Virtual Reality (VR): Used to train operators in simulated environments or view a 3D version of a factory.
Conclusion
A SCADA system is a cornerstone of industrial automation—essential for remotely monitoring, analyzing, and controlling complex technical installations in real time. Whether in energy, water, transport, or industry, SCADA is a strategic tool to improve operational efficiency and ensure service continuity.
👉 Want to learn more?
Discover more about SCADA or contact our experts for a personalized demo