How to configure Sql queries
Data connections enables you to create Sql read and Sql write queries. In general, a Sql read query takes advantage of statements such as SELECT and returns rows from a table, and a Sql write query sends a non-query request, using statements such as INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE, that performs some action on the database and eventually affects rows.
Depending on your data data source and provider, a wizard is available to help you design your query, or you can type the query manually.
The pre-defined Sql read queries are used to map Sql variables. See the topic Linking a Variable to a Sql Read Query for more information.
The pre-defined Sql write queries can be used with Sql variables that have the Command property set. See the topic Linking a Variable to a Sql Write Query for more information.
They can also be used to populate the Grid control in a mimic. See the topic Sql grid control for more information.
Prerequisites
- You have configured a SQL connection.
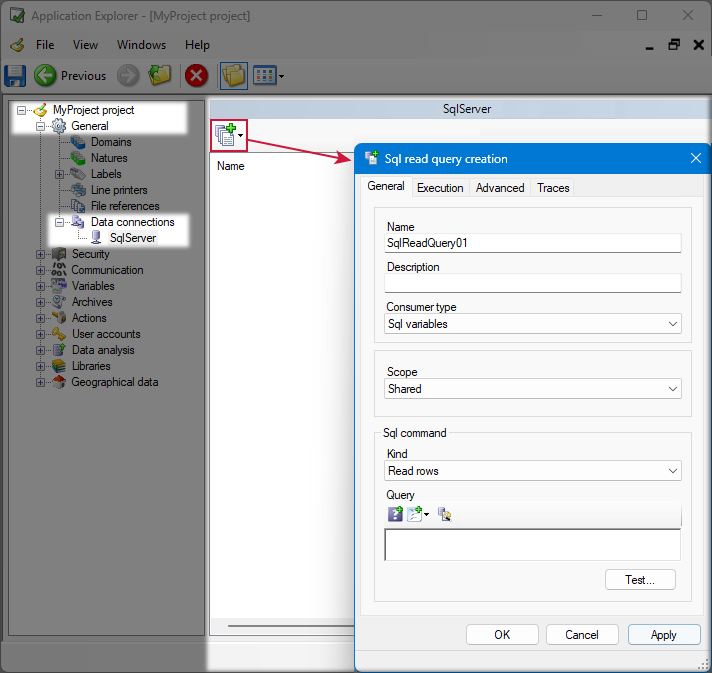
Creating a new query and configuring the general properties
A Sql query used to map Sql variables is able to handle a maximum of 5000 returned values, a value being a field of a row.
For example, a Sql query returning 50 rows with 6 fields each corresponds to 300 values.
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Click on the Add Sql query button in the toolbar and choose whether to add a read or a write query.
 Show picture
Show picture - Enter a query name and (optional) a description. The name is used as the Id of the query throughout the application.
- Select User interface in the Consumer type drop-down If you plan to use this Sql query with the Sql grid control. Only Read queries have this option.
If you plan to use the Sql query with the Sql variables driver, select Sql variables in the Consumer type drop-down. - Select the scope of the Sql query. The scope is used to control the distribution of the Sql query results across user sessions. The scope is not available for User interface consumer type.
- (For a Sql read query) Select the kind of data to be returned by the Sql command:
- Read rows - Used when a query is designed to return a set of rows comprising one or multiple fields.
- Read a scalar value - Used when a query is designed to return a single scalar value.
- Enter a query. The query must respect the Sql syntax as supported by the underlying data source and ADO.Net Data provider. Although the query editor highlights keywords, there is no auto-completion. The maximum query length is 10,000 characters.
- Use the Add a substitution parameter button to add a parameter to the query.
- Use the Add snippet button to insert a predefined Sql query snippet. Query snippets availability depends on the data source and data provider selected when configuring the data connection.
- Use the Open Sql query wizard button to facilitate the configuration of Sql queries. It is useful to create a new query from scratch and cannot be used to modify an existing one. See Using the Sql query wizard to configure a query section to learn more.
The Sql query wizard availability depends on the data source and data provider selected when configuring the data connection.
Once you select User interface in the Consumer type, you only have the Parameters and the Traces tab to configure. The Parameters tab only appears if you have entered a parameter in the Query field.
The scope of the following variables must match the scope of the query: Inhibiting bit variable, triggering bit variable, execution status variable, and execution error variable.
Refer to Linking a variable to a Sql read query and Configuration Items Affected by Scope for more information about the Scope property.
The Kind property is not available for User interface consumer type, only reading rows is of interest.
We recommended to use tools such as a query editor and query performance profiler provided with your data source to design and test your queries. It will help you tune them before you configure the Sql queries in the Application Explorer. In general, poorly designed Sql requests negatively affects the system performances and availability, and in particular the time it takes the external source to process them.
As part of the query editing for certain built-in providers, you have the possibility to insert emojis.
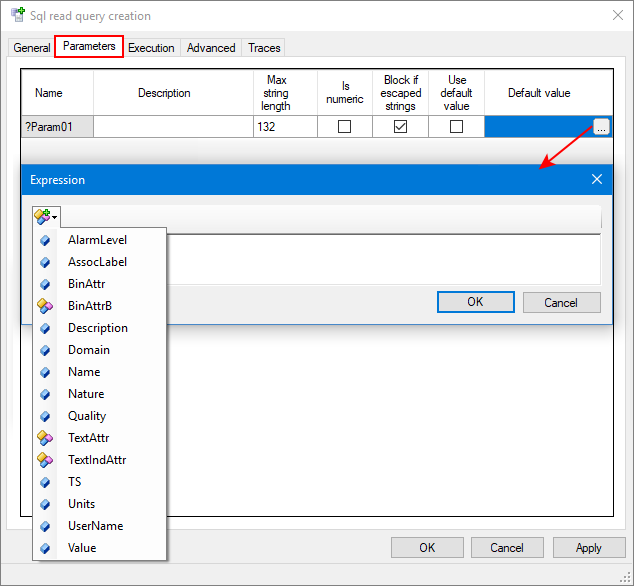
Configuring the query parameters
Parameter configuration allows the value of one or more fields within the query to be provided by the query execution context (for example the variable mapping).
The Parameters tab only appears if you added substitution parameters in the Query field in the General tab.
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Select and open a Sql query, then click on the Parameters tab of the Sql query creation dialog. Here you can configure the parameters added in the General tab. You can enter a description as well as define the following properties:
 Show picture
Show picture - Max string length - The maximum number of characters between 1 and 2048. The default is 132.
- Is numeric - If ticked, the parameter is checked to verify that its contents is numeric.
- Block if escaped strings - If ticked, a parameter value containing an escape string will be blocked and the query will not be processed, for example if the parameter value includes: \0, 1F, 7F, simple or double quotes. If not ticked, the parameter values are not verified, they may contain escape string and be more susceptible to Sql injection risks.
- Use default value - If ticked, the Default Value is used if the value of the parameter cannot be resolved.
- Default value - A value, expression or an empty string.
The default value is useful as a fallback if the parameter value cannot be resolved at runtime. For this reason, while the fallback can be an expression, we recommend not to reference an element that may not be resolvable at all times and in all circumstances.
For example, if a parameter is defined by an expression to calculate a timespan depending on the timestamp of a variable (a query to retrieve data for the previous 10 minutes since a variable value has changed), a good fallback is to use TsNow(Ts_Utc) as default value because it will be a good approximation in many cases. Using the timestamp of another variable may not be helpful as default value if you consider that a variable may not be initialized.
In particular, defining the default value of a parameter by an expression that includes the value of the parameter itself will never work properly (circular dependency).
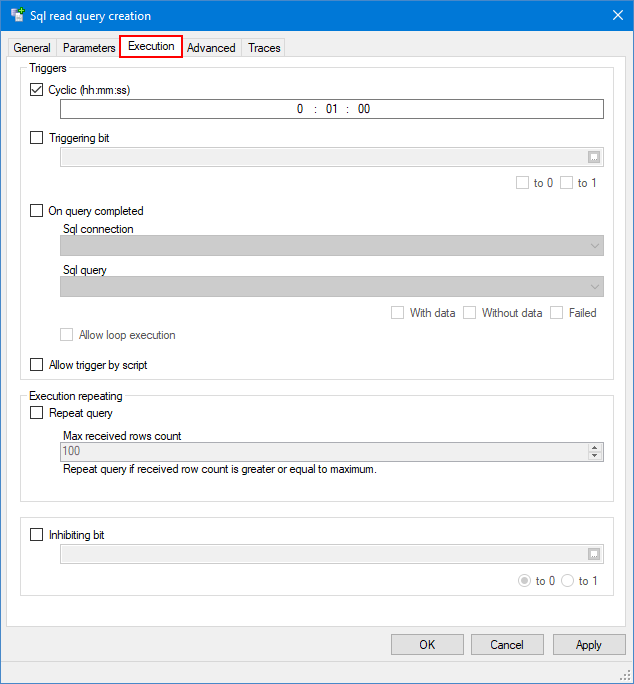
Configuring the execution properties
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Select and open a Sql query, then click on the Execution tab of the Sql query creation dialog. Here you can configure when a query is executed. A query can be executed cyclically, on event and/or upon completion of another query. You can configure the following properties to fine tune query execution:
 Show picture
Show picture - Cyclic - The cycle period is configurable from 10 seconds to 1 hour. There is no synchronization. For example, if you configure the period to be 0:10:00 (10 minutes) and the application start-up was at 12:05:15, the first execution will be at startup, the next one at 12:15:15, 12:25:15 etc.
- Triggering bit - The name of a bit variable used to trigger the execution upon value change.
- On query completed - If ticked, the query is executed upon completion of the query you select here. The condition under which the query is triggered depends on the execution status of the selected query. For example, you can trigger the query when the selected one succeeded and returned no row, or if it failed. The following matrix indicates if the query is executed depending on the configuration and results of the first query. Selection can be combined, for example to execute the query if no row is returned and also if the query failed:
| Query executed with success At least 1 row returned | Query executed with success 0 row returned | Query failed to execute | |
| (For Sql read queries only) If With data is selected (For Sql write queries only) If With affected data is selected | The query is triggered | ||
| (For Sql read queries only) If Without data is selected (For Sql write queries only) If Without affected data is selected | The query is triggered | ||
| If Failed is selected | The query is triggered |
- Allow loop execution - If ticked, allows query chaining that can potentially lead to an infinite loop. It should not be selected if you do not control query chaining precisely. But for example, it is necessary if you configure the query to be called on completion of a query that is itself chained on the execution of the query you are configuring.
- Allow trigger by script - Enable the query to be triggered using the SQL_QUERY SCADA Basic instruction.
- (For Sql write queries only) Allow trigger by variable change - Enable the query to be triggered if a mapped variable changes. Depending on the variable mapping, the query may be triggered on variable command or on value change or both.
- (For Sql read queries only) Execution repeating - The Sql query can be configured in such a way that the execution is repeated if the number of received rows exceeds a maximum you define. It is useful if your query is designed to retrieve a certain amount of rows in nominal mode (with a Select TOP clause for example). However, in some rare cases such as a restart after a long period of time or an avalanche of new rows, you need the query to be repeated until all rows stored during the shutdown are retrieved.
- Repeat query - Tick to activate the execution repeating. It can be used for both a cyclic query and a query executed on a triggering bit.
- Max received row count - The threshold, in number of rows received, that will trigger a reiteration of the execution. The execution can be repeated more than once if the received row count is still greater or equal to the defined value.
- Inhibiting bit - The name of a bit variable that may be used to inhibit execution.
Irrespective of the configuration in the Execution tab, a query is only executed once it has been mapped to at least one variable if it has parameters defined.
Contrary to a Sql read query, if there is no parameter defined, a Sql write query is executed if a trigger condition is met, even if no variable is mapped.
A query triggered in background is not executed if it is still running from a previous execution.
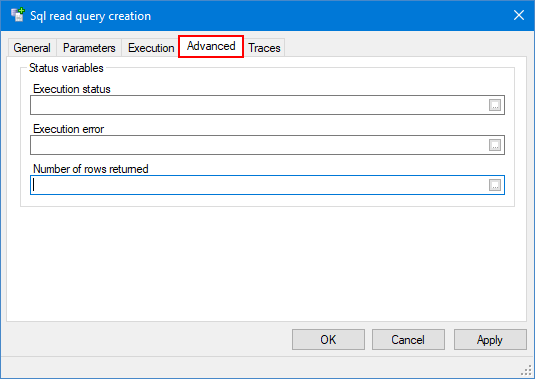
Configuring the advanced properties
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Select a Sql query, then click on the Advanced tab. Here you can select variables to provide information about the status of the query, and queuing properties if trigger by script is enabled in the Execution tab. You can configure the following properties:
 Show picture
Show picture - Execution status - The status that can be provided are:
- 0 = Successful.
- 1 = Running.
- 2 = Failed.
- 3 = Canceled.
- Execution error - A text variable providing additional information when the status variable indicates a failure. In most cases, the error text itself comes directly from the ADO.NET Data provider.
- Number of rows affected - A register variable providing the number of rows returned by the last execution of the query. Set to 0 if the query has failed.
Each query has its own queue. When flow regulation is active, all query requests (calls) are queued and actually executed in the order they were added to the queue.
Expression parameters for a query are evaluated at execution time and not when queuing.
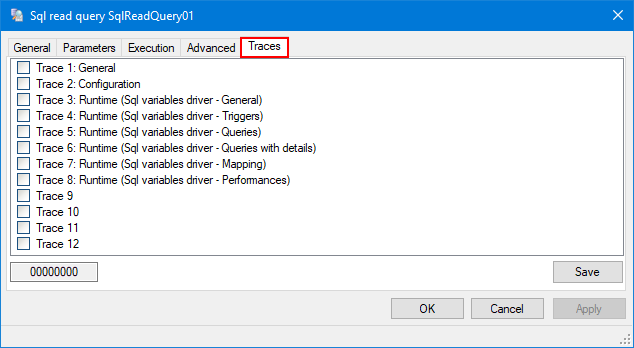
Activating traces
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Select a Sql query, then click on the Traces tab. Here you can enable diagnostic trace messages. Each trace generates specific messages that are logged in the Trace Files and displayed in the Event Viewer dialog (F7).
 Show picture
Show picture
The following are some of the traces you can activate:
- Trace 1: General - Enable general traces related to the handling of the Sql query.
- Trace 2: Configuration - Enable traces specific to the configuration handling of the Sql query.
- Trace 3: Runtime (Sql variable driver - General) - Enable general traces related to the Sql variable driver activity for this query.
- Trace 4: Runtime (Sql variable driver - Triggers) - Enable traces related to the triggering of this query for the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 5: Runtime (Sql variable driver - Queries) - Enable traces related to the handling of this query for the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 6: Runtime (Sql variable driver - Queries with details) - Enable detailed traces related to the handling of this query for the Sql variable driver, including parameter substitutions and value extractions.
- Trace 7: Runtime (Sql variable driver - Mapping) - Enable traces related to the mapping resolution of this query for the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 8: Runtime (Sql variable driver - Performances) - Enable traces related to performances of this query for the Sql variable driver.
Using the Sql query wizard to configure a query
The Sql query wizard is a Sql query designer that helps you create a new query in a few clicks, even if you are not familiar with the Sql syntax.
The Sql query wizard availability depends on the data source and data provider selected when configuring the data connection. It may or may not be available for the data provider you are using.
The datasource must be available to use the Sql query wizard. Iif necessary, a connection is established to browse tables and other elements that are the base for building queries.
- Go to Configure, then select the Application Explorer and expand the configuration tree to select an existing Sql connection on the Data Connections node.
- Click on the Add Sql query button in the toolbar and choose whether to add a read or a write query, then click the button Open Sql query wizard in the Sql command section to start designing your query.
- Choose a table from the drop-down and use the control icons on the right of the table to select and order the data. The Add calculation column button allows you to add calculated columns based on tables columns.
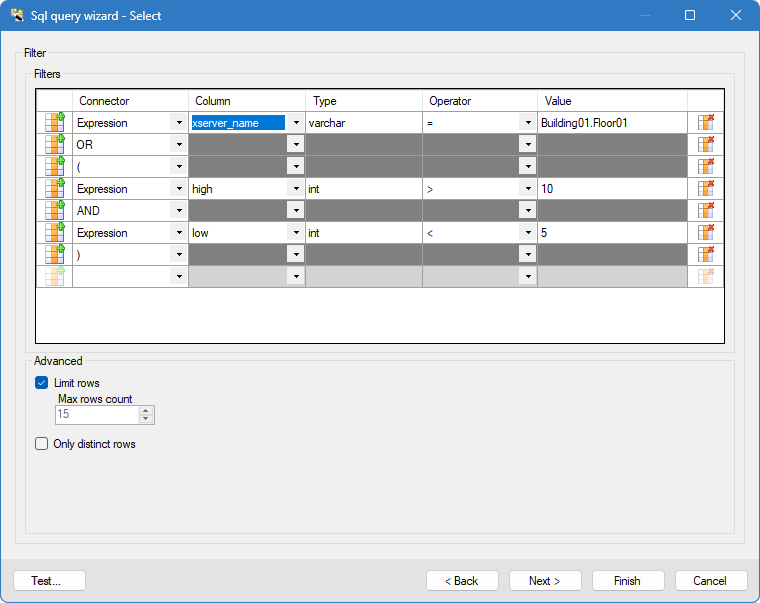
- Click Next, select your Sql query elements using the drop-down fields of the table to filter the data to return (Where clause). You can also set the max number of rows to be returned and whether to only return distinct rows.
 Show picture
Show picture - Click Next, define how you want to order and group results using the arrows on the right of the tables then click Finish.
- Select whether the Sql query is designed to insert, update, or delete rows. The Sql query wizard dialog opens.
- Select from the drop-down, the table to modify and depending on the action selected in the previous dialog, you can:
- Insert data by selecting column names and entering values for the selected columns.
- Delete data by filtering the table selected to identify the rows to delete.
- Update data values by selecting columns and entering or replacing a value. Values can be set to null or replaced by the value of a parameter.
- Click Finish.
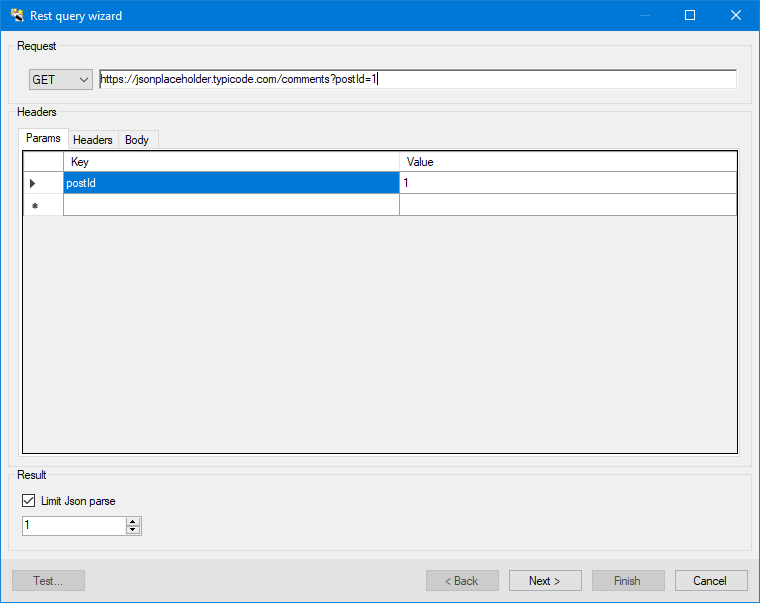
- Select a REST API method. The following HTTP methods are available: Get, Put, Post, Patch, and Delete.
- Enter the full API Uri, including query parameters. The Params grid is instantly populated with the query parameters included in the Uri of the request.
 Show picture
Show picture - In the Header tab, add key and value pairs for headers required by the API.
- In the Body tab, enter the body string (if required by the API). There are three possible formats: application/json, text/plain, or x-www-form-urlencoded.
- In the Results pane, enter a limit for parsing nested JSON. See the documentation of the provider you are using for more information.
- Click Next, select the fields you need from the query result. The Add calculation column button allows you to add calculated columns based on tables columns.
- Click Next, select your Sql query elements using the drop-down fields of the table to filter the data to return (Where clause). You can also set the max number of rows to be returned and whether to only return distinct rows.
- Click Next, define how you want to order and group results using the arrows on the right of the tables then click Finish.
At any point in the wizard, you can test your queries by clicking the Test button in the bottom left corner. This opens the Sql query test dialog, where you can input parameter values and view the query results along with execution status details.
For a typical Sql-based datasource such as Sql Server instance or an Oracle database server, the configuration is the following:
For a Sql read query:
For a Sql write query:
For CHAR/VARCHAR field types, use single quotes around 'null' to store it as a string rather than a NULL value.
For a typical REST-based API, the configuration is the following:
The configuration for read and write queries is similar, with the key difference being the method used. Write queries typically use POST, PUT, or PATCH, along with a body payload for data. Write requests generally don't include filtering or ordering, as these apply to data retrieval.
You can rename the fields and use the control icons on the right of the table to order them.