Linking a Variable to a Sql Write Query
A variable, that has the Command property set, can be linked to a Sql write query by choosing the Sql Variables source. See the topic Data Connections Overview. When a variable is linked in this way, its properties including the real-time value can be stored in a third party data source such as Microsoft's SQL Server. Write queries can be configured so that they are executed periodically, on event and/or when the variable changes (either due to a command or a change of the value).
The configuration is in two steps.
- Selects the Sql Connection and its subordinate Sql Write query.
- Parameters - Configuration of any parameters that the query contains. Parameters are used, instead of the mapping used in a Sql read query, to write the variable value to the database.
See the topic Sql variables Write query mapping examples for a detailed explanation and examples.
Using variables with a Sql write query is subject to scope-related constraints:
-
The scope of the Sql write query and the scope of the mapped variable must match,
-
When using a variable to set the value of an input parameter, constraints related to scope apply to avoid user-specific data to be used as inputs in a context where the query results will be accessible to other users.
The following matrix summarizes the list of valid combinations of scopes:
| Scope of the variable | Scope of the Sql write query | Scope of the variables used to set input parameters |
| Local | Local | Local, Shared |
| Shared | Shared | Local, Shared |
| Session | Session | Local, Shared, Session |
| Client-context | Client-context | Local, Shared, Session, Client-context |
How to configure the Data selection
- Open the configuration dialog for the variable and select the Source tab.
- Select Sql Variables as the Source. Sql Variables is only available if one or more Sql connections have been configured.
The new tabs Reading and Writing appear for configuration of the data selection. Select the Writing tab.
 Show picture
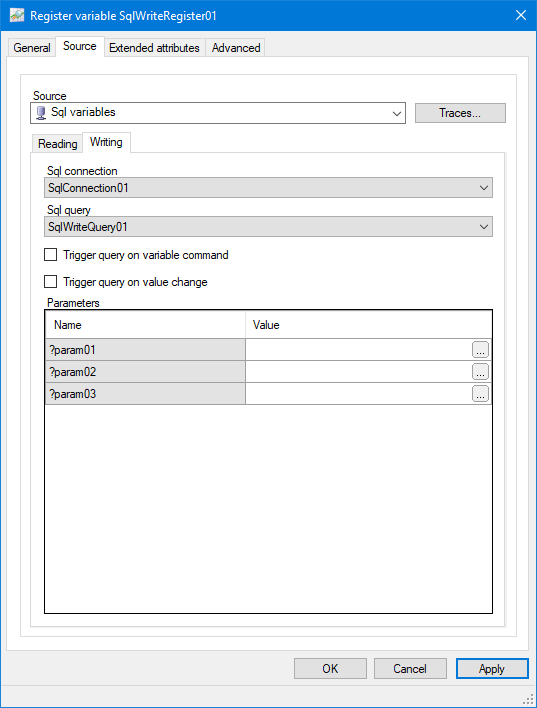
Show picture - Select the Sql connection and the subordinate Sql query. Any parameters required by the Sql write query appear in the Parameters list.
 Show picture
Show picture - Select, if any, the conditions under which the query will be triggered. You can trigger the query when a command is sent by a user for the variable (Trigger query on variable command) and / or the value changes (Trigger query on value change). If you do not select either of these, the query will only be triggered under the conditions configured in the query itself. See the Execution tab in the topic How to configure Sql queries.
Trigger query on value change is only triggered if the value change is the consequence of processing a read query. It's purpose is to allow the execution of a write query on completion of a read query that has changed the value.
To enable the trigger of a query on either variable command or value change, the corresponding property must also be set in the write query configuration.
How to configure the Parameters
If one or more parameters are found in the Sql write query, they are listed must be substituted using an expression. A parameter can only be substituted once. If the query is subsequently used in another variable, the parameter substitution is pre-configured and the field is dimmed indicating it is read only.
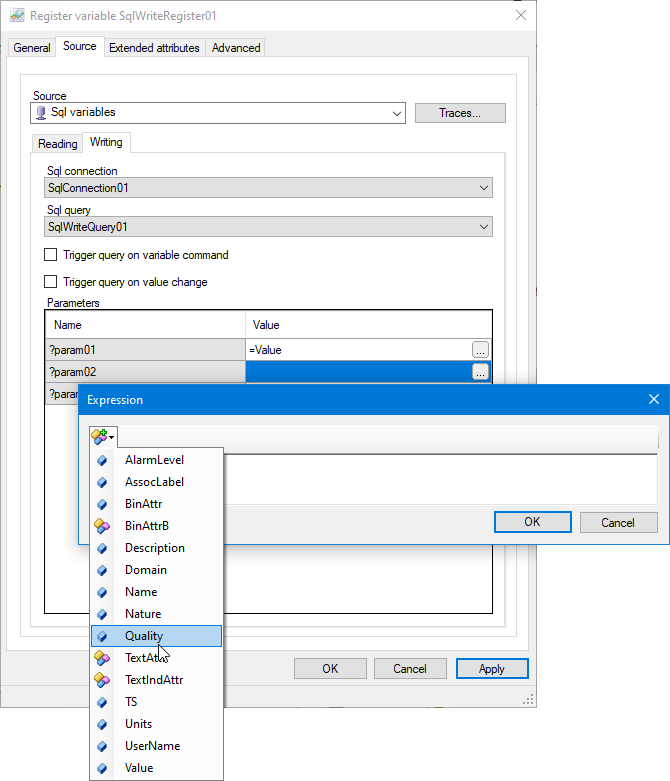
A parameter defined by an expression can reference a property of the variable (domain, Extended attribute etc.) and use the functions and operators of the expression engine. The button at the top left of the expression editor dialog displays a list of the variable properties that can be substituted. ![]() Show picture
Show picture
A description of the available variable properties can be found in the topic Linking a Variable to a Sql Read Query.
Parameters can only be set once - the first variable in which a query is used will set the value of the parameter.
For example, Register01 has the domain Security. Register01 uses a query containing ?Param01 configured to use the Domain. The value substituted for ?Param01 will be Security. Register02 uses the same query. Irrespective of the domain of Register02, Security will be used as the value for ?Param01.
If a parameter is mapped with an indirection on a Text extended attribute so that it is set with a variable value, the adequacy of the scope of the variable with regards to the scope of the Sql query is only verified at run-time. It is not checked at configuration time, nor at start-up time.
Traces
The Traces button allows you to enable diagnostic trace messages. Each trace generates specific messages that are logged in the Trace Files and displayed in the Event Viewer dialog (F7).
- Trace 1: All drivers - General - Enable general traces related to the activity between the Variable Manager and the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 2: All drivers - Details - Enable detailed traces related to the activity between the Variable Manager and the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 3: All drivers - Performances - Enable traces related to performances of the Sql variable driver.
- Trace 4: Sql variable driver - Performances - Enable traces related to performances of the Sql query results processing.