Standalone, Client-Server and Redundant Architecture Examples
This topic describes some of the most common architectures. Architectures based on a web server and web clients are described in the topic Web Based Architecture Examples.
There are many variations to fit system requirements in term of:
- Number of users
- Type and number of operator stations (HMI)
- Availability
- Flexibility
- Scalability
- Resilience
- Maintenance and application life cycle management
Contact the technical support for more information.
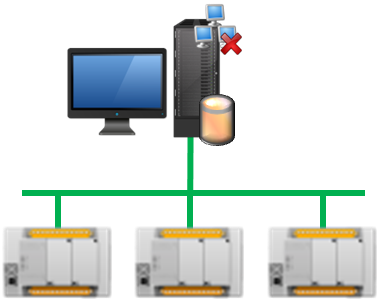
Standalone station
Standalone stations are usually operator panels, it is the simplest architecture with all functions and roles integrated into a single station.
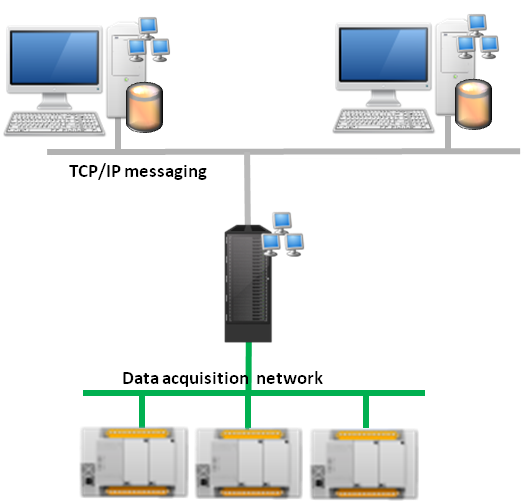
Multi-station
The simplest client/server architecture, to be employed as soon as more than one user seat is required.
A usual variation is to separate Data Acquisition and Historical Data production on 2 different servers, or to have clients produce historical data locally.
Multi-station with a Remote Desktop Server for deploying client stations
This architecture, from the PcVue networking point of view is the same as the previous one except that as a way to rationalize the deployment of client station, RDS and lightweight terminals are used.
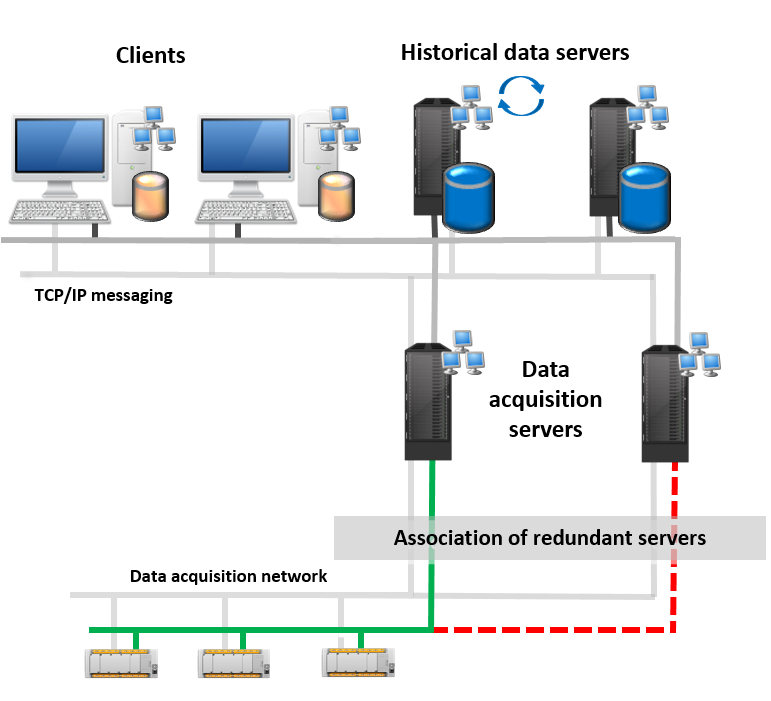
High availability
When a higher availability and resilience are required, this architecture, more distributed, brings redundancy and roles separation.
It is similar to the multi-station architecture but with data acquisition server and historical data server separation and redundancy.
A usual variation is to also include a Web Server and Web clients, thus combining permanent operator's seats and one-off user connections.
Mutualized server
The mutualized architecture is an interesting variation of the high-availability.
When you have to monitor and control multiple processes, production lines, plants, buildings, sites... and can benefit from a reliable network, you can set up a high-end server that will be used as the standby server for multiple other zones. By mutualizing the standby server, you achieve redundancy and availability while minimizing the overhead of deploying and maintaining a fully duplicated set of servers.
Three level
When network segmentation is a concern, a gateway can be added to the architecture.
Such an architecture is useful when, for example, the system spans over a Wide Area Network, or when data consumers (client stations or data repository) are located in a less-trusted network.
Such a gateway can be deployed in a DMZ, and if necessary gateways can be redundant.
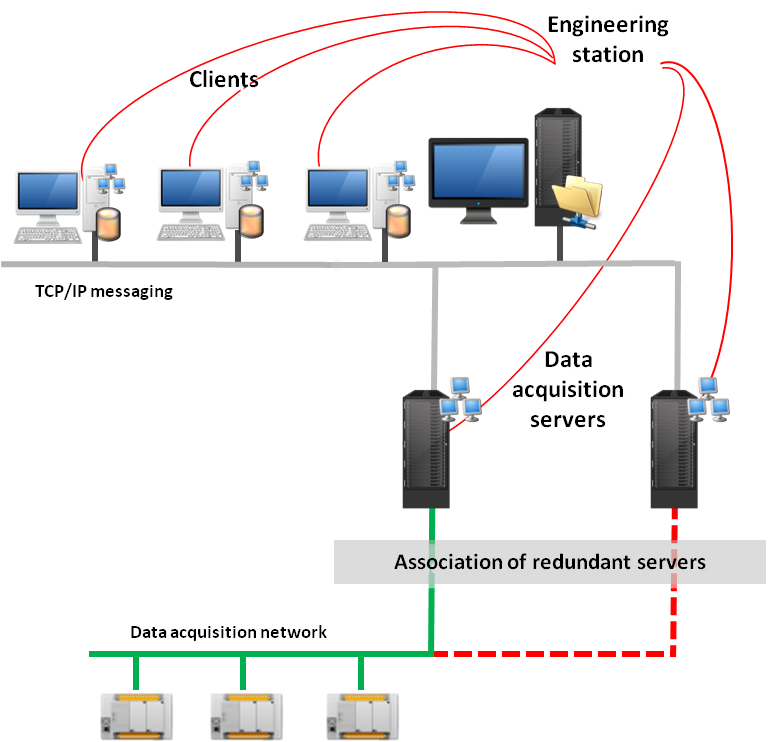
Engineering station with version management
To make the maintenance and the deployment of a project easier and faster, central project management can be used. Different versions of a project are centralized in a shared directory on the network. Usually a dedicated engineering station is used to host the central project versions directory and to make the change for a project. Any station can load and run automatically a version of a project from the central project directory.