How to import a Beckhoff TwinCAT configuration
The Smart Generator for TwinCAT allows you to import a TwinCAT project file to generate the following PcVue configuration elements:
- Data acquisition network, devices, and frames for the Beckhoff TwinCAT driver.
- I/O variables including mapping onto frames.
- The TwinCAT Variable Definition files. As the addressing in TwinCAT frames is alias (name) based, and those in PcVue are address based, an additional file is generated for each frame which provides a correspondence between the TwinCAT alias and the PcVue frame address.
The TwinCAT project file *.tpy as generated by the TwinCAT programming environment versions 2.11, 3.0 and 3.1 is supported.
For 3.x versions of TwinCAT, only the legacy IEC 61131 standard is supported. The latest additions to the TwinCAT 3.x standard as well as data types including OOP, C++, C and Simulink cannot be taken from this file. TwinCAT 3.x instead offers a different symbol file with the extension *.tmc.
Supported data types
Data types LINT, ULINT and multi-dimension ARRAY are not supported.
Scalar data types
| TwinCAT type | PcVue variable type | Range | Frame data type |
| BIT | Bit | 0..1 | Boolean |
| BOOL | Bit | 0..1 | Boolean |
| BYTE | Register | 0..255 | Unsigned 8 bit integer |
| WORD | Register | 0..65535 | Unsigned 16 bit integer |
| DWORD | Register | 0..4294967295 | Unsigned 32 bit integer |
| SINT | Register | -128..127 | Signed 8 bit integer |
| USINT | Register | 0..255 | Unsigned 8 bit integer |
| INT | Register | -32768..32767 | Signed 16 bit integer |
| UINT | Register | 0..65535 | Unsigned 16 bit integer |
| DINT | Register | -2147483648..2147483648 | Signed 32 bit integer |
| UDINT | Register | 0..4294967295 | Unsigned 32 bit integer |
| REAL | Register | Float.Min..Float.Max | 32 bit float |
| LREAL | Register | Double.Min..Double.Max | 64 bit float |
| STRING | Text | \0 Terminated string | |
| TIME | Register | 0..Float.Max | 32 bit float |
| TIME_OF_DAY | Register | 0..Float.Max | 32 bit float |
| DATE | Register | 0..Float.Max | 32 bit float |
| DATE_AND_TIME | Register | 0..Float.Max | 32 bit float |
Structured data types
| Supported | Not supported |
|
|
Refer to the overview topic Smart Generators overview to learn more.
Selecting the source data
Before you start the import process, we recommend that you back up the PcVue variables configuration in case of any problems occurring during the import process. The variable configuration is stored in the file VAREXP.DAT in the project's C folder.
Make sure that PcVue is shut down before copying the file.
-
Go to Configure then Smart Generators and click New TwinCAT import. The TwinCAT Smart Generator dialog opens.
-
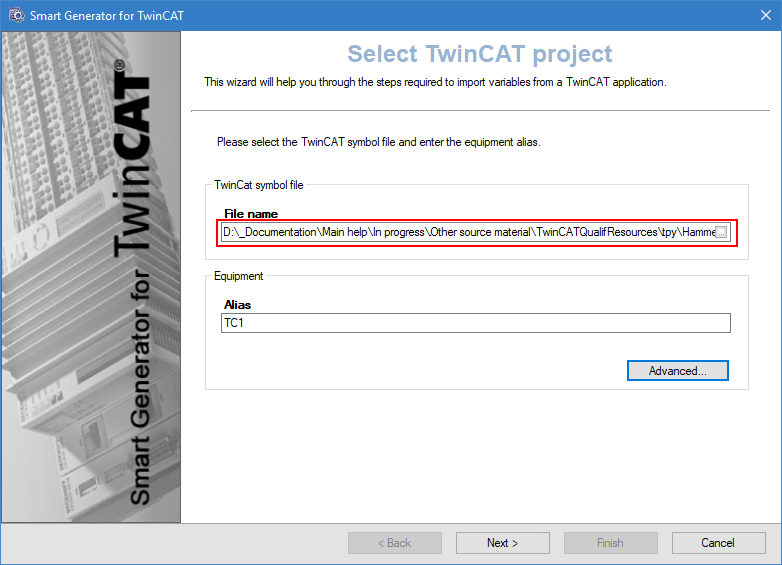
Click on the ellipsis button in File name field, then select the .tpy file that contains the TwinCAT project file to import.
 Show picture
Show picture -
Enter an Alias for the equipment. This is the name by which the device will be known in PcVue.
-
Click the Advanced/Options button, then select a server list and a client list in the Networking list tab to define the behavior of PcVue variables for a multi-station project.
The lists of servers and clients must already have been created in PcVue and the station from which you run the smart generator must be in the servers list.
-
Select the Advanced options tab and set the device's Port, AMS Net ID if you want to override values that will be imported from the TwinCAT Symbol file. Check Use custom attributes if you want to filter imported elements based on the Custom attribute, and click OK to validate.
If you select Use custom attributes, only symbols that have the keyword SV_Import set to True in the .tpy file will be imported. Others will ignored. Refer to the section TwinCAT Smart Generator custom attributes below for more information.
Defining branches and selecting variables
After you have selected the source data and configured the networking lists and options of the import via the Select project dialog, the next step is to define the branches and select the variables you want to generate.
-
Click Next, the Branch Management dialog opens. This step allows you to control how branches and variable names are derived from source data names so that the generated variables fit in the branching and naming logic of your project. First, you can enter a global branch if you want to prefix the name of all generated variables with a particular branch segment. You can also select branch separator options to control how source data names will be split into branch segments:
-
Use numeric characters as branch separator - If selected, a branch separator will be added after each numeric character. For example, a source data named MOT1DEFAULT1 will generate a variable named MOT1.DEFAULT1.
-
Use specific sequence character as branch separator - If selected, the sequence of characters you select will be replaced by a branch separator. For example, if you select the underscore ('_') as sequence character, a source data named CONTROLROOM_COMMAND will generate a variable named CONTROLROOM.COMMAND.
A branch separator is not added when a numeric character is at the end of the name.
-
-
Click Next, the variable import process is initialized and the Select import type dialog opens. Select the type of import you need:
- Custom import if you want to access the Select variables dialog in which you can filter and manually select the list of variables to import.
- Full import if you want to generate variables for all source data.
-
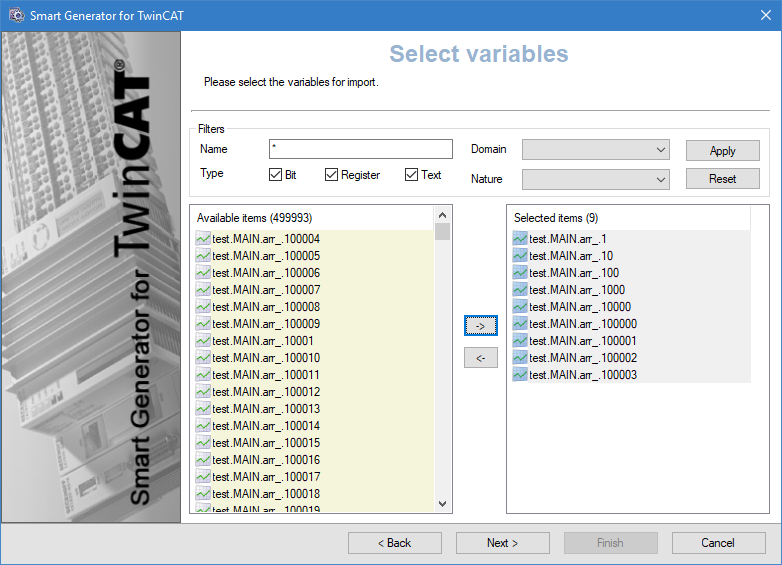
(Custom import option) Adjust the filters to find the variables to import. The Name field allows to filter the list of variables according to the name in the source data. You can use wildcards, the asterisk (matches any number of characters) and the question mark (matches a single character).
For example:
'Pump1' would only match a source data named 'Pump1'.
'Pump?' would match 'Pump1' or 'Pump2' etc. but not 'Pump10'.
'Pump*' would match 'Pump1', 'Pump2' and 'Pump10' but also 'Pumpkin'.The variables that match the filter appear in the Available Items pane.
-
(Custom import option) Select the variables filtered in the Available items pane for import and click the right-arrow -> button. The variables in the Selected items pane are to be imported and generated.
Renaming and generating variables
After you have defined the branch and selected variables to generate via the Select variables dialog, the next step offers the possibility to edit the variables you have selected and prepare them for generation.
If a variable is displayed in red, it means that it is invalid for use in PcVue and will not be generated. Use the Rename variables dialog to ensure variable name compliance:
- The max length of a variable name is 255 characters.
- The max number of branch elements in a variable name is 12.
- The name of a branch element or the name of the leaf element cannot be empty (length =0) or exceed 255 characters.
- The name of a variable can only include letters, digits, or the underscore.
- Variable names shall be unique. Two variables cannot have the same name.
-
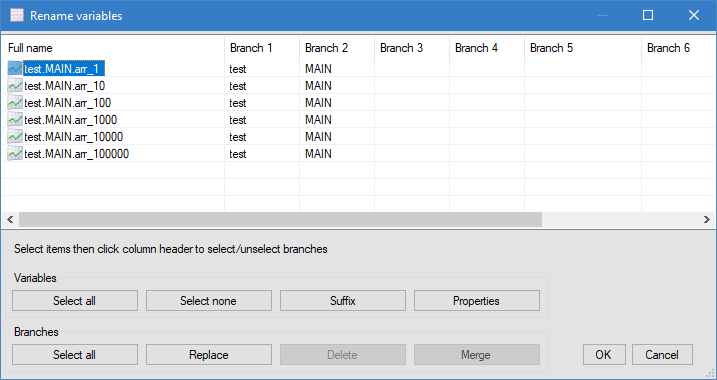
Click Next. The Generate variables dialog opens, listing all variables selected for generation. To rename variables, either select variables and click Rename selected, or use the Rename invalid button. The Rename variables dialog displays variables in a grid and offers several actions.
-
The Rename variables dialog is designed to make it easy to give a final polish to variable names and fix invalid ones, and also to bulk modify variable properties, to set the Command level or Alarm property for example.
The following operations are available:
- To modify a single variable, double click it, or select it and click Properties. You can edit its name in the General tab. Click OK to validate.
- To add a leaf to one or more variables (to add a .Cmd or .AlarmTmpHigh for example), select them, then click Suffix and enter the suffix to be added. Click OK to validate.
- To replace characters in the name of one or more variables, select them, then click Replace to open the Replace dialog. Enter the strings to search and replace, then click OK.
- To replace branch segments, select the variables, then select the branch segments to be replaced by clicking on the column header and click Replace to open the Replace dialog. Enter the strings to search and replace, then click OK.
- To delete a branch segment, select the variables, then the branch segments to be removed by clicking on the column header and click Delete. The selected branch segments are then removed from the selected variables.
- To merge branches, select the variables, then the branch segments to be merged by clicking on the column header and click Merge. The selected branch segments are then deleted for the selected variables. You can only merge consecutive branch segments.
You can edit the variable properties in the Details tab. These properties can be its type, domain, nature etc.
You can use Shift+click to select a group of adjacent variables and branches or Ctrl+click to select several individual variables.
Once you are done editing the variables click OK to close the dialog.
-
Click Finish and Yes in the Generation dialog to start the generation of variables in PcVue. A dialog is displayed indicating the progress. Any variables in the smart generator that already exist in PcVue are discarded. The corresponding variables in PcVue are not overwritten or updated in any way.
Any variables appearing in red are invalid and will not be generated when clicking Finish.
Synchronizing an existing import
When you synchronize an import, the smart generator compares the configuration elements available in the import file with those that have been imported previously to PcVue.
The synchronizing process takes into account any filter that you may have used previously with the import. For example if there are 400 variables in the import file and the previous use of the import was with a filter and created 100 variables in PcVue, synchronization will inform you that there are 300 new variables available for import.
-
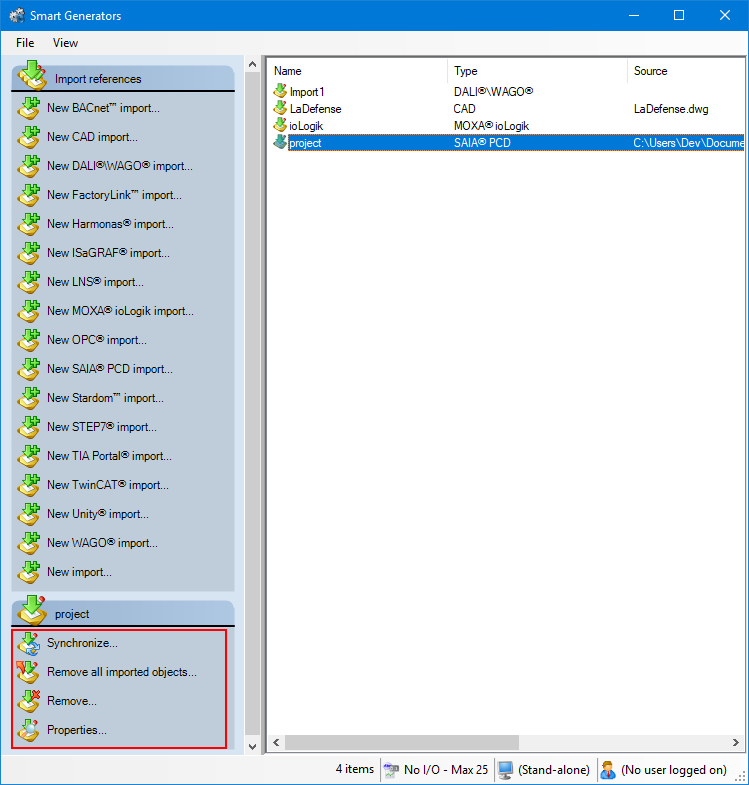
Select the import to synchronize in the right pane of the Smart Generators dialog. A list with actions appears under the Import references pane.
 Show picture
Show picture -
Click Synchronize. This will open the smart generator dialog in which you can reconfigure the import. If variables have been added to the import file since the last import, the smart generator will display the Import new variables dialog, inviting you to make either a full or a custom import of the remaining variables.
-
If you select full import, all variables not already in PcVue are imported.
-
If you select custom import, you can filter the variables using the Select variables dialog.
-
If the smart generator finds variables in PcVue that no longer exist in the import file, a list of the variables is displayed. Using this list, you can choose to remove some or all of the variables from PcVue.
You can choose to only remove imported configuration elements of a smart generator without removing the smart generator import itself. This can be done by right-clicking the import generated and selecting Remove all imported objects.
TwinCAT Smart Generator custom attributes
The TwinCAT Smart Generator allows you to define custom attributes for each data point symbol in the *.tpy file. The information is stored in the comment field of the TwinCAT symbol which is used for passing metada from TwinCAT to 3rd party systems.
The syntax of the custom attributes consists of a set of key/value pairs in the typical TwinCAT format. The syntax has been defined so as not to interfere with other items that use the comment field.
Supported keywords
| Name | Values | Types | Description |
| SV_Import | true | false | Standard and complex |
Indicates if it is to be used in the import. If the property Use custom attributes is set the following logic is used to include or exclude symbols. If used on a complex type all included variables are affected.
|
| SV_VariableName | string | Standard | Replaces the variable name. |
| SV_Branch | string | Complex | Passes a branch name to a structured type where it is used with concatenation of the variable name of the nested standard types. |
| SV_BranchDescription | string | Complex | Passes the branch description to a structured type where it is used as prefix for all the variable descriptions in this branch. |
| SV_VariableDescription | string | Standard | Text to be used as variable description. |
| SV_Alarm | true | false | Standard (Boolean only) | Sets the Alarm property of the variable. |
| SV_Log | true | false | Standard (Boolean only | Sets the Log 0>1 and Log 1>0 properties of the variable. |
| SV_Command | true | false | Standard (Boolean only) | Sets the Command property of the variable. |
| SV_Domain | string | Standard and complex | Sets the Domain property of the variable. If used on a complex type all variables are affected. |
| SV_Nature | string | Standard and complex | Sets the Nature property of the variable. If used on a complex type all variables are affected. |
String values are not required to be enclosed in quotes.
Example of a TwinCAT file with custom attributes
You can define custom attributes for each data point symbol anywhere you would like in TwinCAT.
VAR_GLOBAL
Heating_circuit_01_VAL AT%MB0:REAL;(*~(SV_Import:true) (SV_Variable:UV018Heating_circuit_01_temperatureflow) (SV_Description:
Heating_circuit 01 temperatureflow) (SV_Alarm:False) (SV_Log:True) (SV_Command:False)*)
Heating_circuit_02_VAL AT%MB0:REAL;(*~(SV_Import:true) (SV_Variable:UV018Heating_circuit_02_temperatureflow) (SV_Description:
Heating_circuit 02 temperatureflow) (SV_Alarm:False) (SV_Log:True) (SV_Command:False)*)
END_VAR