BACnet Device Advanced Properties
The following screenshot was taken with the default configuration. ![]() Show picture
Show picture
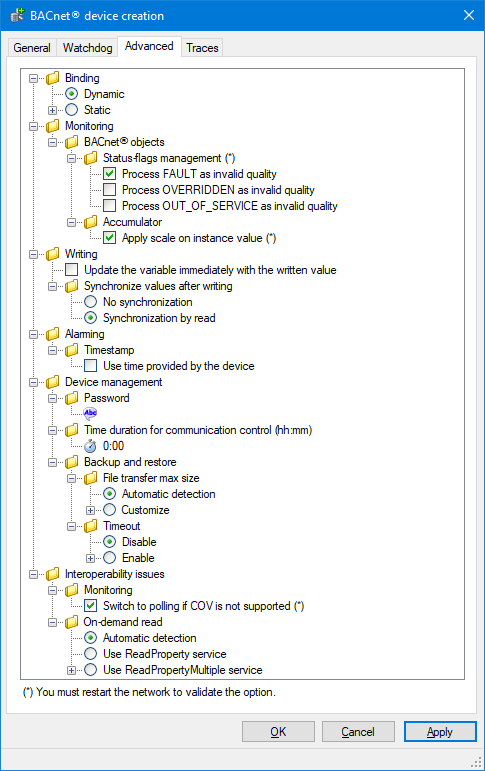
- Binding
- Dynamic - Use the classic BACnet binding mechanism based on UDP broadcast messages to browse the devices on the BACnet network.
- Static - Use the static device binding mechanism to communicate directly with an IP device without soliciting the classic BACnet browsing based on UDP broadcast messages.
- MAC address - The device BACnet MAC address, which can be entered in one of two formats:
- The socket address under the form IP address:UDP port. For example 10.59.5.151:47808
- As the actual BACnet MAC address. For example 0A:3B:05:97:BA:C0
Note that the BACnet MAC address format, as defined by the standard, is a conversion of the socket address as six bytes, and does not match the MAC address as defined usually.
IP address: 10.59.5.151 > 0A:3B:05:97
Port : 47808 > BA:C0
- The socket address under the form IP address:UDP port. For example 10.59.5.151:47808
- Network identifier - The BACnet network number or network Id. By default, 0 is used to indicate the local network (as defined in the BACnet standard).
- MAC address - The device BACnet MAC address, which can be entered in one of two formats:
- Monitoring
- BACnet objects
- Status flag management - Configure how the BACnet device status flags are interpreted.
- Process FAULT as invalid quality.
- Process OVERRIDDEN as invalid quality.
- Process OUT_OF_SERVICE as invalid quality.
- Accumulator
- Apply scale on instance value - Calculate the value of a variable mapped to the object by using the PresentValue and the Scale properties.
- Status flag management - Configure how the BACnet device status flags are interpreted.
- BACnet objects
- Writing
- Update the variable immediately with the written value - For a variable configured with polling, when a command is sent successfully, setting this property updates the variable value immediately with the written value (otherwise you have to wait for the next poll).
- Synchronize values
after writing – Used to synchronize the client and server after a write
has been performed.
- No synchronization – No action taken.
- Synchronize by read – The value in the client is read back from the server cache. This is the default selection.
- Alarming
- Timestamp
- Use time provided by device - Use the timestamp included in the event notification.
- Timestamp
- Device management
- Password - The password for all services that are password protected, such as ReinitializeDevice and DeviceCommunicationControl.
- Time duration for communication control (hh:mm) - Used for DeviceCommunicationControl to indicate the number of minutes that the remote device shall ignore all APDUs other than DeviceCommunicationControl and, if supported, ReinitializeDevice APDUs. If the “Time Duration” property is 0, then the time duration is considered indefinite, meaning that only an explicit DeviceCommunicationControl or ReinitializeDevice APDU will enable communications.
- Backup and restore
- File transfer max size
- Automatic detection - Automatically detect the file transfer behavior when receiving backup files or sending restore files.
- Customize - Force the number of bytes, or the record count, according to the access mode defined by the BACnet File object (stream or record access).
- Stream access (bytes) - The number of bytes if using stream access.
- Record access - The number of records if using record access.
- Timeout - Configure a specific timeout for the backup/restore process. The backup/restore process can take much longer than other requests.
- Disable - Disable specific timeout.
- Enable - Enable a specific timeout. The value is entered in minutes.
- File transfer max size
- Interoperability issues
- Monitoring
- Switch automatically to polling mode if COV not supported - Force monitoring by polling if COV is not supported or if COV subscription limit in the device has been reached.
- On-demand read - Defines which BACnet service shall be used for reading properties on-demand, for example to fill-in property grids in Helpers and other design and diagnostic tools.
- Automatic detection - The driver will determine the most adequate service depending on the BACnet device capabilities. Default selection.
- Use ReadProperty service - The ReadProperty service will be used even if a more suitable service is supported by the device.
- Use ReadPropertyMultiple service - The ReadPropertyMultiple service will be used, and the action may fail if the device does not support this service.
- Monitoring
In some cases, using static binding can be a good alternative to setting up a BBMD. See BACnet BBMD Configuration for more information.