Topic
[KB100]Using Supervisor LAN Connection Through a TCP/IP Network via a Router
| Applies to:
PcVue all versions supporting Windows XP, 2000 and NT 4.0. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Summary:
This articles describes the configuration that is required when using a LAN connection between PcVue stations on a TCI/IP network via a router. |
||||||
|
|
||||||
| Details:
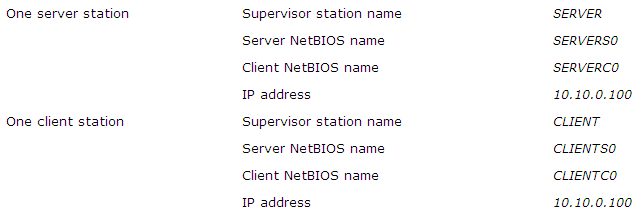
The configuration process uses the NetBIOS interface. Each station is defined by a unique name called a NetBIOS name. In a multi-station configuration, each station has an associated name such as STATION1. (A station can be a client, a server or both client and server).
The value 0 in S0 and C0 represents the network card number (default 0). PcVue’s LAN communication uses Broadcast messages. Each message from a station to another station is broadcast on the LAN network. Every station connected to the same sub-network receives the message. Only the addressed station replies. By default, stations connected to a different sub-network do not receive the messages. Nevertheless, message exchanges between different sub-networks are possible with an additional configuration file. It consists of a table that associates each NetBIOS name with an IP address.
In the table NetBIOS names.IP address, only the server’s NetBIOS name is necessary. In the example, it is STATION1S0. A way of doing this is to define the table in a file called LMHOSTS. Using LMHOST.SYS under Windows XP, 2000 and NT 4.0.
The syntax of the file is as follows: IP Address NetBIOS name. Notes
Example With these parameters:
On the server station, LMHOSTS would contain: 10.10.0.100 SERVERS0 On the client station, LMHOSTS would contain: 10.10.0.101 CLIENTS0
A combined LMHOSTS file would contain: 10.10.0.100 SERVERS0
How to test connections You may use the PING command to perform a basic test, from the MSDOS Prompt window. On the client station use these commands: PING <server IP address> Each command should give a PING answer as follows: answer <IP address> : byte = 32 time < 10ms TTL=128 |
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Created on: 22 Oct 2010 Last update: 26 Aug 2024